Figure 7. Oral administration of aspirin improves locomotor activities in C57/BL6 and A53T-Tg mice.
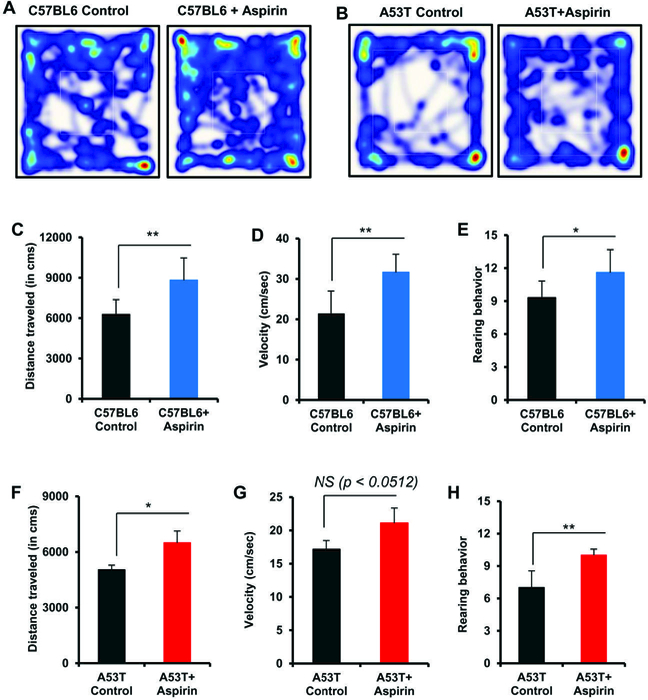
Male C57/BL6 (A, C-E) and A53T-Tg (B, F-H) mice (n=5 per group) were treated with aspirin (2 mg/kg body wt/d) mixed in 0.5% methylcellulose orally via gavage. Control mice received 0.5% methylcellulose as vehicle. After 30 d of treatment, locomotor activities were monitored (A & B, track plot; C & F, distance traveled; D & G, velocity; E & H, rearing). Results are mean ± SEM of five mice per group. **p<0.01 (= 0.00518) vs control (C); **p<0.01 (= 0.00312) vs control (D); *p<0.05 (= 0.03509) vs control (E); *p<0.05 (= 0.01560) vs control (F); **p<0.01 (= 0.00197) vs control by two-tailed paired t-tests. NS, not significant.
