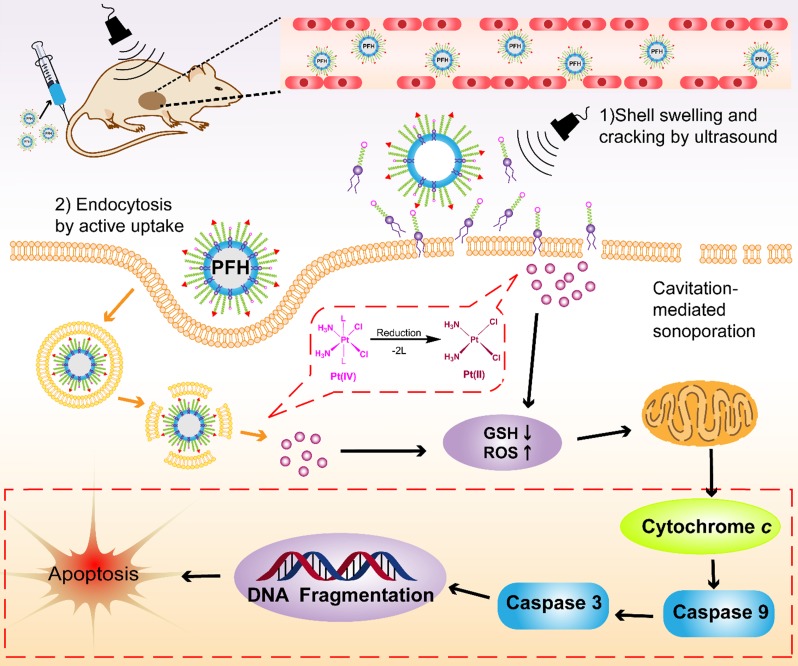
Figure 8.
The schematic illustration of Pt(IV) NP-cRGD assisted by US for tumor treatment. The Pt(IV) NP-cRGD are rapidly accumulated at the tumor sites via the EPR effect and active targeting and then uptaken by tumor cells through two main pathways: (1) Prodrugs are taken up by passive diffusion and sonoporation after ultrasound exposure and interact favorably with and adsorb onto the cancer cell membrane; (2) Pt(IV) NP-cRGD are selectively taken up via receptor-mediated endocytosis. Next, the prodrug and nanoparticles that escape from the endosome respond to endogenous GSH and release the drug. Finally, Pt(IV) NP-cRGD with US induce ROS overproduction and cause cell apoptosis to maximize the antitumor efficiency.