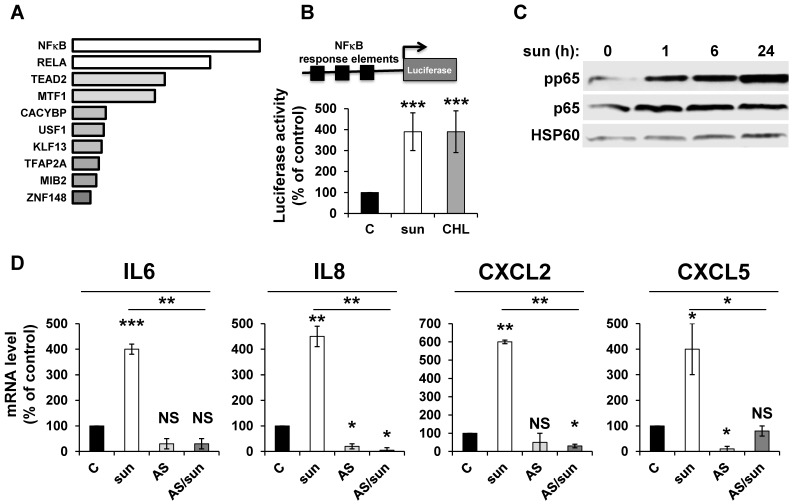
Figure 2.
Adaptation to sunitinib depends on a genetic program involving the NFκB transcription factor. (A) NFκB and RELA were the most enriched transcription factors following sunitinib treatment (2.5 μmol/L for 48 hours). (B) A reporter gene containing three NFκB binding sites was transfected in untreated (C), sunitinib (sun, 2.5 μmol/L) or chloroquine-treated (CHL, 10 μmol/L) 786-O cells treated for 48 hours. The percentages or normalized luciferase counts are shown. (C) 786-O cells were incubated in the presence of sunitinib 2.5 μmol/L for the indicated times. The total (p65) and phosphorylated (pp65) forms of NFκB were detected by immuno-blotting; HSP60 is shown as a loading control. (D) 786-O cells were left untreated (C) or incubated for 48 hours in the presence of sunitinib (2.5 μmol/L) combined or not with AS602868 (AS, 2.5 μmol/L). The mRNA levels of IL6, IL8/CXCL8, CXCL2 and CXCL5 were evaluated by qPCR. P values are indicated; * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001.