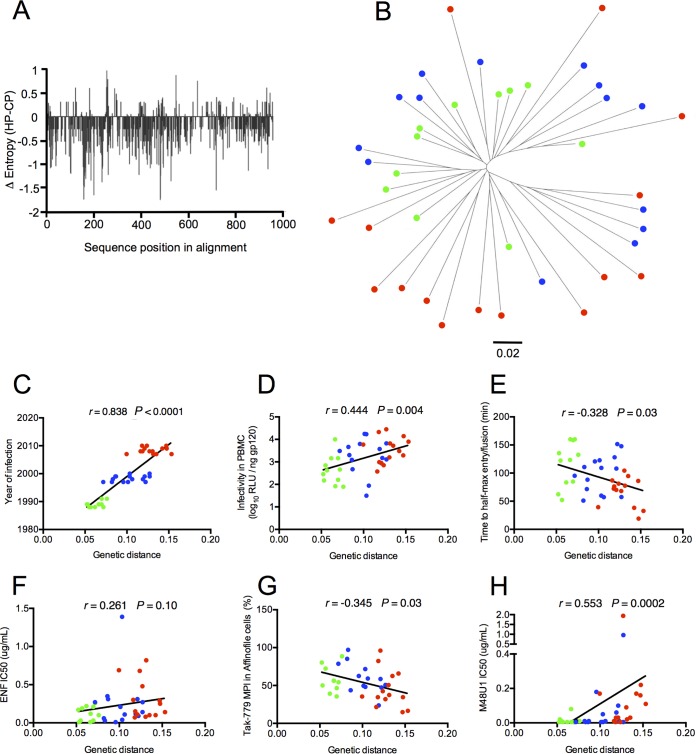
FIG 6.
Diversification of Env pseudotypes is associated with their increased infectious properties. (A) Plot showing the difference in Shannon entropy between Env sequences derived from historical patients (HP; n = 11) and contemporary patients (C; n = 14) at each position in an alignment of these two sets of sequences. (B) Midpoint-rooted maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of full-length env sequences. The 40 full-length env sequences of the transmitted viruses included in our study were aligned. A maximum likelihood tree was constructed using MEGA7. Env sequences from historical patients (HP; n = 11), intermediate patients (IP; n = 15), and contemporary patients (CP; n = 14) are identified by different colors (HP in green, IP in blue, and CP in red). Branch lengths correspond to nucleotide substitutions per site, as indicated in the scale. Correlation between env genetic distances from the MRCA and the infection year of patients (C), the infectivity in PBMCs (D), the time to half-max entry (E), the resistance to ENF (F), TAK-779 MPIs in Affinofile cells (G), and the resistance to M48U1 (H).