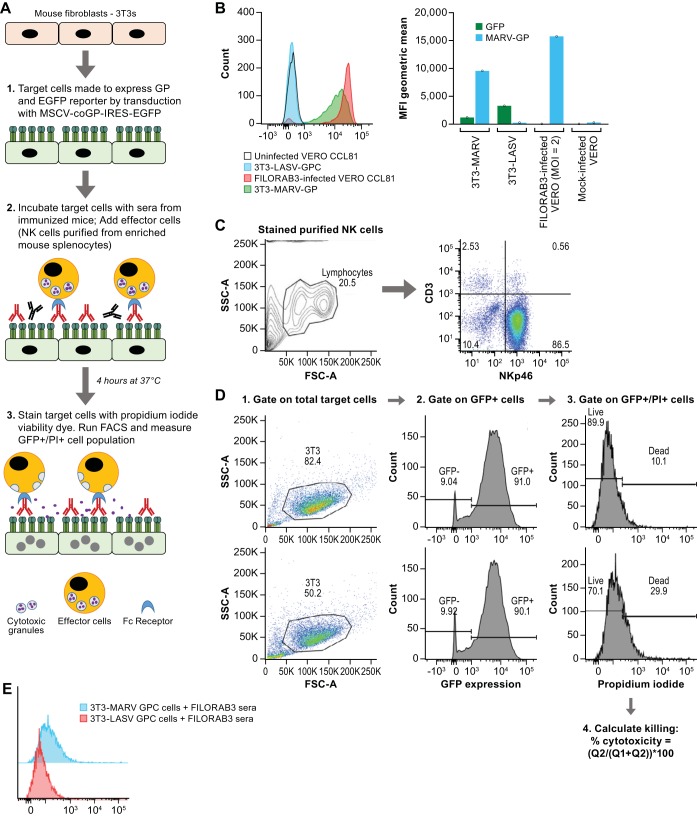
FIG 9.
Characterization of in vitro NK cell-mediated ADCC assay. (A) Schematic depicting the experimental procedure and corresponding biological events for our in vitro mouse ADCC direct killing assay. IRES, internal ribosome entry site; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting. (B) (Left) MARV GP expression in transduced mouse 3T3 target cells was confirmed by flow cytometry (green curve) using an anti-MARV GP mouse monoclonal antibody (MAb 3E10). 3T3 target cells expressing a nonspecific viral glycoprotein (LASV GPC) were stained with MAb 3E10 and assayed as a negative control. Vero CCL81 cells infected at an MOI of 0.1 for 48 h were fixed and stained with MAb 3E10 and assayed as a positive control for MARV GP expression. (Right) Bar graph derived from flow cytometry plots showing the geometric mean of the medium fluorescence intensity (MFI) for both GFP and MARV GP. (C) Phenotypic characterization by flow cytometry on magnetically purified NK cells enriched from splenocytes of naive BALB/c mice to determine the purity of NK cells in the effector cell population for the ADCC assay. CD3 and NKp46 biomarkers were used to identify the percentage of effector NK cells in the population. (D) Gating strategy on MARV-infected 3T3 cells for ADCC assay. Percent cytotoxicity was determined by the percentage of GFP+/PI+ cells in the total parental GFP+ cell population. The top row is a representative flow plot of killing in MARV-infected 3T3 target cells incubated with negative-control sera. The bottom row is a representative flow plot of killing in target cells incubated with purified IgG derived from pooled sera from BALB/c mice immunized with FILORAB3. (E) Overlapping PI histograms of MARV-infected 3T3 and LASV-infected 3T3 cells incubated with FILORAB3-purified IgG (1:100) showing the difference in cytotoxicity. Forty thousand target cells were used in the assay. SSC-A, side scatter area; FSC-A, forward scatter area; Q1, quadrant 1; Q2, quadrant 2.