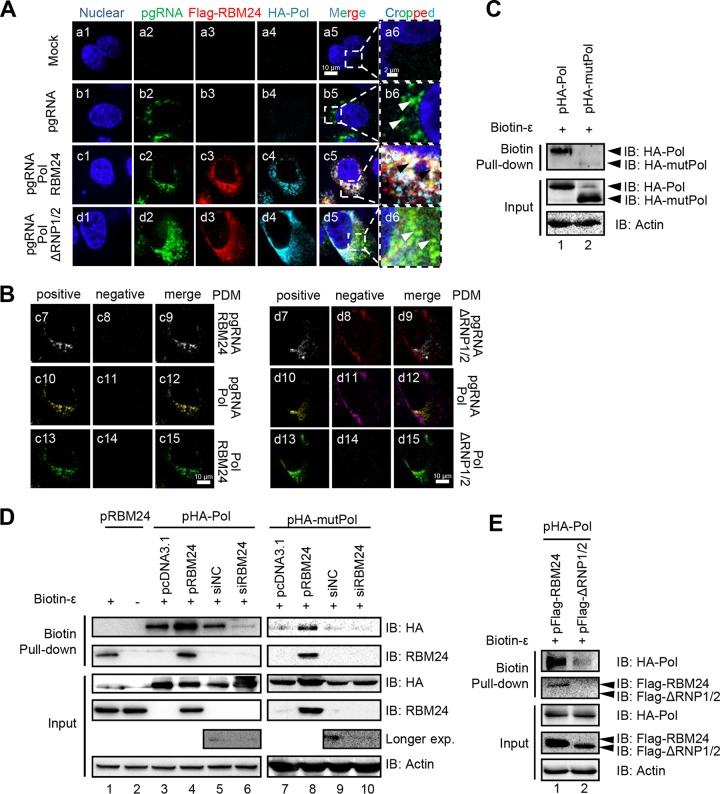
FIG 4.
RBM24 promotes Pol-ε interaction and formation of the Pol-RBM24-ε complex. (A) HepG2 cells were cotransfected with P−C− (the HBV C-null and Pol-null construct that was used to express the pgRNA), pHA-Pol, and pFlag-RBM24 or pFlag-ΔRNP1/2. At 48 hpt, the cells were fixed and subjected to IF staining and RNA FISH. An anti-HA antibody and an anti-Flag antibody were used as primary antibodies for the staining of Pol and RBM24, respectively. A probe targeting the 5′ end of pgRNA was used for pgRNA staining. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258. Higher-magnification images of the selected area are also shown. Bars, 10 μm for panels a1 to a5, b1 to b5, c1 to c5, and d1 to d5 and 2 μm for panels a6, b6, c6, and d6. (B) The product of the difference from the mean (PDM) for the two channels (pgRNA/Pol, pgRNA/RBM24, or RBM24/Pol) in panels c5 and d5 was analyzed. Volocity software generated a positive (c7, c10, c13, d7, d10, and d13) and a negative (c8, c11, c14, d8, d11, and d14) PDM channel. (C to E) HEK293T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids or siRNA were lysed, followed by a biotin-ε pulldown assay using Dynabeads M-280 streptavidin. The input or pulled-down proteins were detected by Western blotting. Actin served as a loading control.