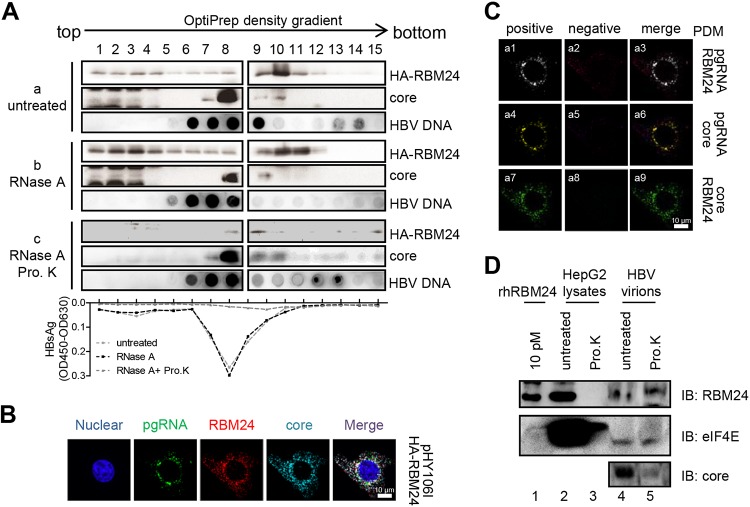
FIG 7.
RBM24 is incorporated into the capsid. (A) pHA-RBM24 was transfected into HepAD38 cells, and cell lysates were subjected to an OptiPrep density gradient and treated without or with RNase A or RNase A plus proteinase K (Pro. K). The gradients were fractionated into 15 fractions. For each fraction, HA-RBM24 and the core protein were detected by Western blotting, HBV DNA was detected by dot blotting, and HBsAg was detected by an ELISA. OD450, optical density at 450 nm. (B) HepG2 cells were cotransfected with pHY106 and pHA-RBM24. At 48 hpt, the cells were fixed and subjected to IF staining and RNA FISH. An anti-HA antibody and an anti-Flag antibody were used as primary antibodies for identifying Pol and RBM24, respectively. A probe targeting the 5′ end of pgRNA was used for identifying pgRNA. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258. (C) The PDM for the two channels (pgRNA/core, pgRNA/RBM24, or RBM24/core) was analyzed. Volocity software generated a positive (a1, a4, and a7) and a negative (a2, a5, and a8) PDM channel. (D) HBV virions were purified from serum of patients with HBV infection. A total of 50 μg of HBV virions (lines 4 and 5) or 100 μg of HepG2 cell lysates (lines 4 and 5) was digested with or without proteinase K, and the samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE. Purified rhRBM24 was loaded as a control. RBM24, the positive control eIF4E, and core were detected by Western blotting using the anti-RBM24 antibody, anti-eIF4E antibody, and anticore antibody.