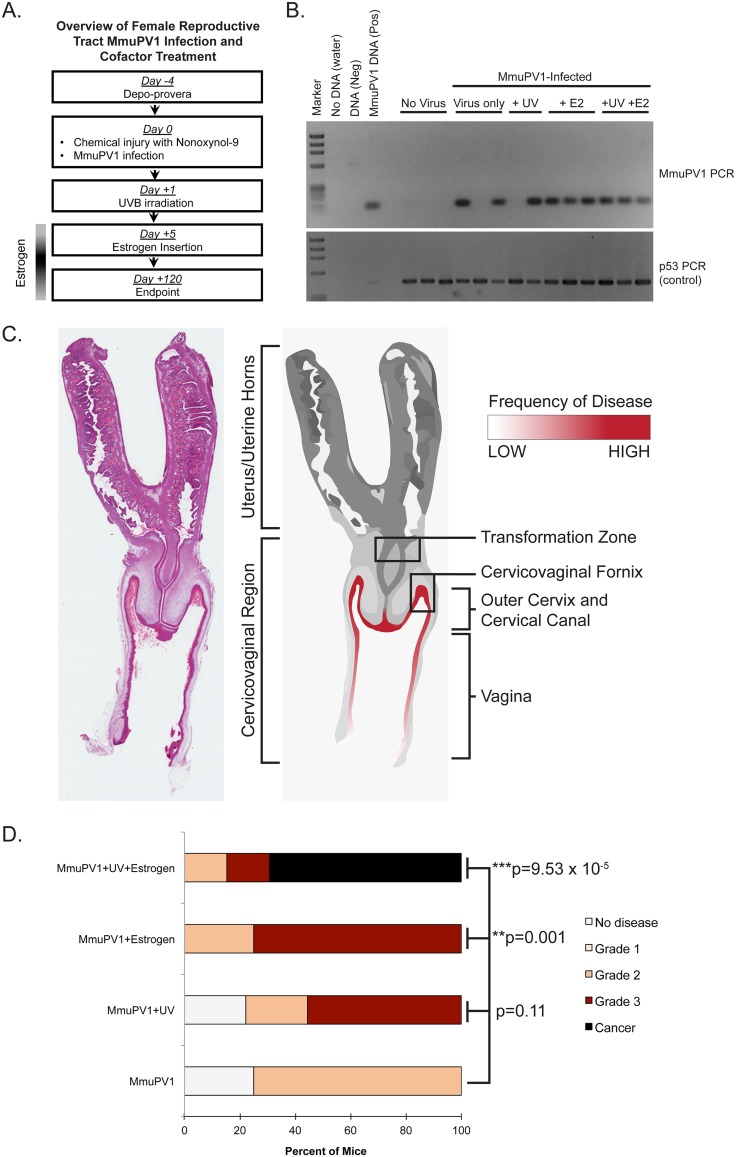
FIG 2.
MmuPV1 infects and causes neoplastic disease in the murine female reproductive tract of immunocompetent mice alone and in combination with UVB and estrogen treatment. (A) Overview of MmuPV1 infection of female reproductive tract in FVB mice combined with cofactor treatment. When applicable, mice were irradiated with 1,000 mJ/cm2 UVB 1 day postinfection, and estrogen insertion was performed 5 days postinfection. (B) DNA was isolated from cervicovaginal lavage samples and analyzed by PCR for the MmuPV1 E2 gene (top) or for the p53 gene (bottom) to verify DNA presence/quality. (C) Anatomical location of MmuPV1-induced neoplastic disease development in the female reproductive tract of FVB mice. A full-slide scan of a representative H&E-stained murine female reproductive tract is shown on the left. A rendering of this reproductive tract is shown on the right. Regions of epithelia where disease developed in FVB mice are highlighted in red, where the intensity of red shading corresponds with the frequency of disease observed at each site. (D) Disease severity in cohorts of MmuPV1-infected mice as determined by histopathological analysis. Statistical analysis for overall disease severity was performed using a two-sided Wilcoxon rank sum test. For numbers of mice per group, please refer to Table 1.