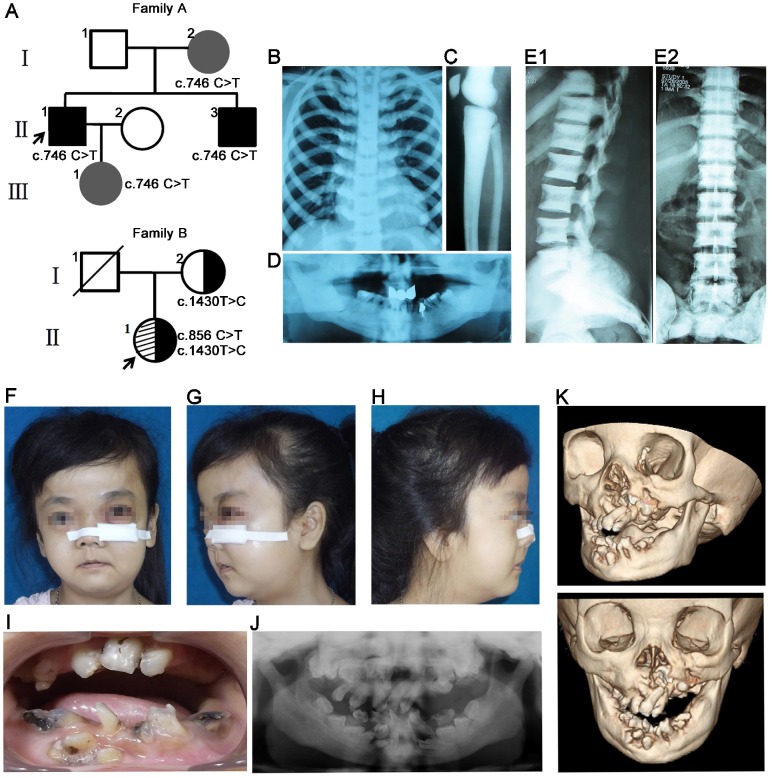
Figure 1.
Pedigree and clinical examinations. (A) Pedigree maps. Family A presented an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance with c.746C>T mutation in CLCN7 gene. Black and grey represented severe phenotypes and no complaint of symptoms, respectively. The proband (II1) in family B carried compound heterozygous mutations in CLCN7 gene (c.856C>T; c.1430T>C) and the variant c.1430T>C in exon 16 was inherited from her mother. (B-D) Radiographic images of II1 in family A. Increased bone density in chest (B) and long bones (C). Malformation of craniofacial bones and tooth abnormalities in orthopantomography of II1 (D). (E1-E2) Radiographic images of II3 in family A. Sandwich vertebral changes. (F-K) Clinical images of individual II1 in family B. (F-H) Typical craniofacial deformities including macrocephaly, frontal bossing, and changes in shape and proportions of facial skeleton. Osteomyelitis and fistulae in the left facial bones. (I-J) Intraoral photography and orthopantomography showed malocclusion and tooth malformation. (K) Hypoplasia of facial skeletons from CT images.