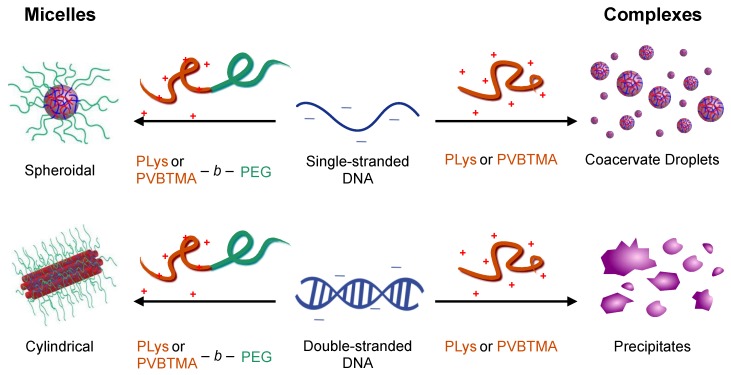
Figure 1.
Polyelectrolyte complexation and PCM nanoparticle formation. DNA is a highly charged polyanion. When mixed with polycations (right), polyelectrolyte complexes are formed (macrophase separation). When mixed with cation-hydrophilic neutral block copolymers (left), microphase separation produces PCMs. In both scenarios, the hybridization state of the nucleic acid (single- vs. double-stranded) determines the nature of the product (liquid droplets vs. solid precipitates for the complexes, spheroidal vs. cylindrical PCMs). This study compares the effect of hydrophilic (poly(lysine), PLys) and hydrophobic (poly((vinylbenzyl) trimethylammonium), PVBTMA) polycations in determining the properties of the complexes and PCMs.