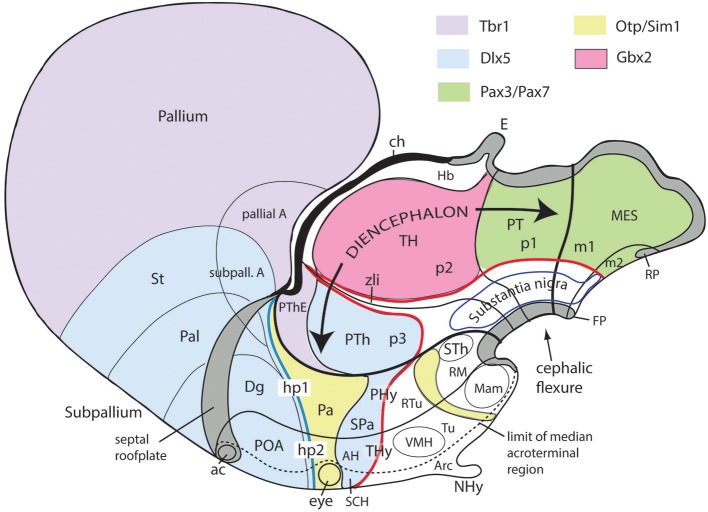
Figure 10.
Schematic map copied from Puelles (2015) of various gene expression patterns that agree with prosomeric analysis of the forebrain (largely centered on alar plate domains of the different prosomeres across midbrain, diencephalon and hypothalamus; no copyright permission required); alar-basal limit in red, though the zona limitans transverse spike (zli) is independent from the basal plate, irrespective of its molecular similarity (Shh expression; see Figure 5B). The mesodiencephalic extent of the dopaminergic substantia nigra and associated ventral tegmental area is mapped, as well as the distinct perimamillary/periretromamillary basal hypothalamic band, in yellow (see text); the separate alar hypothalamic paraventricular area (Pa; also in yellow)shares these particular markers (but not others). Dlx5 is shared among given prethalamic (PTh), hypothalamic (SPa, AH, SCH) and subpallial (St, Pal, Dg, POA) domains typically producing GABAergic neurons. A thick blue line represents the hypothalamo-telencephalic boundary; note telencephalic subpallial inclusion of the POA due to shared gene expression, and local ending of the roof plate at the anterior commissure (ac). Hypothalamic alar and basal subdivisions and some individual nuclei mentioned in the text are identified.