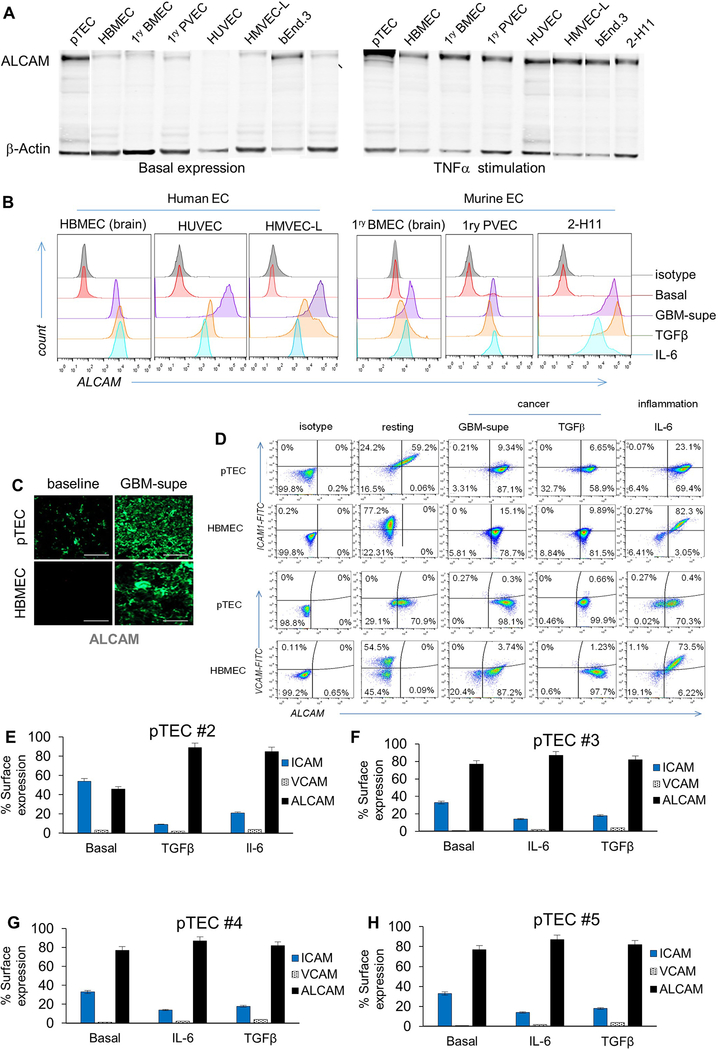
ED-Figure 2 │. ALCAM expression in a panel of human and murine endothelial-cells and their reactivity to inflammatory and cancerous conditioning.
(A) Western Blot for ALCAM in a panel of human and murine EC lines: pTEC (primary Tumor EC from GBM surgical excision), HBMEC (Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial-cells), 1ry BMEC (Primary Brain Microvascular Endothelial-cells), 1ry PVEC (Primary Pulmonary Vein Endothelial-cells), HUVEC (Human Umbilical Cord Vascular EC), HMVEC-L (Human Microvascular EC of the Lung), bEnd.3 (murine brain tumor EC) and 2-H11 (murine SV40-transformed axillary lymph node vascular endothelium). The left panel shows basal ALCAM expression except in tumor EC (pTEC and 2-H11). Right panel shows the induction of ALCAM in all endothelial-cells after incubation with TNFα for 6 hours. (B) Expression of ALCAM at baseline and after 6 hours of conditioning in GBM-supe, TGFβ or IL6. Only tumorous-EC expressed ALCAM at baseline while normal-EC did not. C) IFC for ALCAM in 5×104 pTECs and HBMEC in the in vitro BBB-model at baseline and after culture in GBM-supe. Scale-bar=50μm. (D) Differential expression of key adhesion molecules at baseline and under the influence of cancer and inflammation in pTEC and HBMEC. Flow-cytometry dot plots detailing of baseline expression of ALCAM, VCAM1 and ICAM1 on 1×104 pTEC and HBMEC and conditioned expression after culture in GBM-supe, TGFβ or IL6. (E-H) Expression of adhesion molecules at baseline and under the influence of cancer and inflammation in pTEC (n=4) acquired from surgical resection samples (pTEC #1 is shown in Figure 1G).