Figure 2.
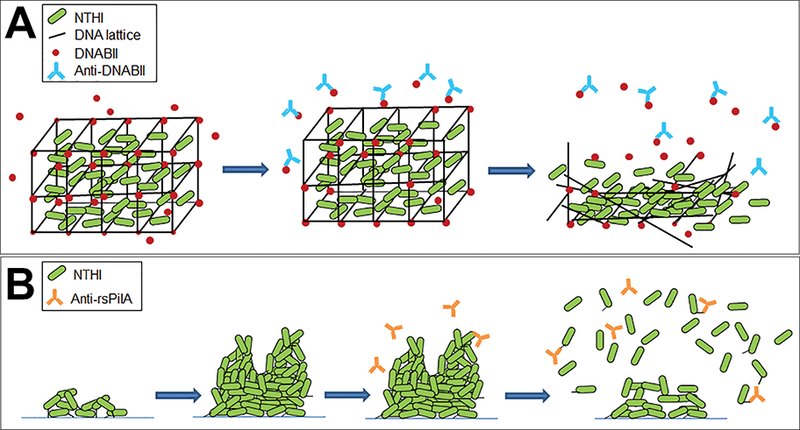
Two distinct mechanisms to disrupt NTHI biofilms. (A) Biofilms formed by many bacterial human pathogens, including NTHI incorporate eDNA (black lines) and DNABII proteins (red circles) within the EPS. Antibodies against DNABII proteins (blue) bind and sequester DNABII molecules from the extracellular milieu and induce an equilibrium imbalance. Release of DNABII proteins from the eDNA scaffold results in catastrophic collapse of the biofilm structure and exposure of resident bacteria. (B) NTHI utilize Tfp to adhere, organize and form a biofilm. Antibodies directed against the majority subunit of NTHI Tfp, PilA, (orange) induce a ‘top-down’ dispersal event that is dependent on quorum signaling.
