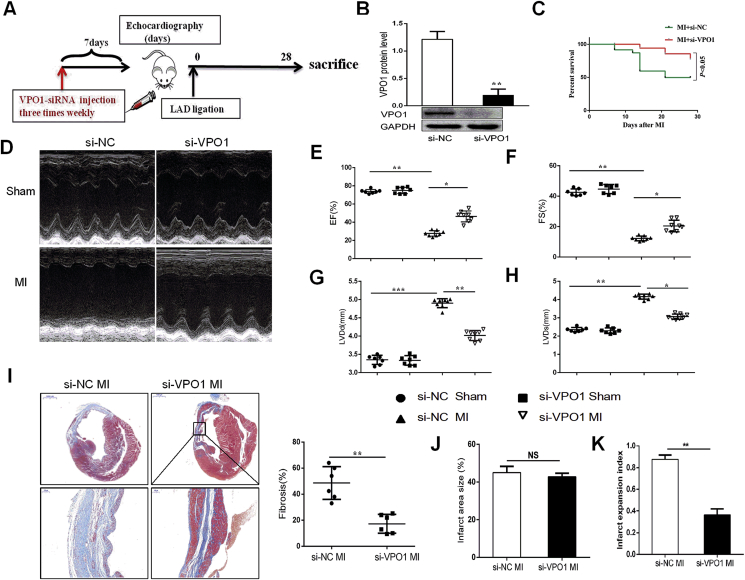
Fig. 3.
Knockdown of VPO1 attenuates cardiac fibrosis and improves cardiac function in vivo. (A) Experimental procedure for injecting mice with siRNA. (B) The efficiency of VPO1 knockdown by siRNA was assessed by western blot and quantified with Image Lab software. n = 6 per group. (C) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of mice injected with si-NC and si-VPO1 28days after MI. (D) Representative M-mode images of sham and MI mice injected with si-NC and si-VPO1. (E–H) Ejection traction (EF), fractional shortening (FS), left ventricular internal dimension at end-diastole (LVIDd) and left ventricular internal dimension at systole (LVIDs) were analyzed by echocardiography. n = 7 in sham group, n = 8 in MI group. (I) Representative images of Masson trichrome at various magnifications. n = 6. Upper scale bar:1 mm, bottom scale bar: 100 μm. Quantification of the total fibrotic area using Image Pro Plus. (J) Quantification of infarct area size (infarct area/total area) of left ventricle. (K) Quantification of infarct expansion index ((LV cavity area/total heart area) ✖ (uninfarcted septal thickness/infarcted LV free wall thickness)). n = 6. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. In B, Student's t-test in comparison with si-NC group. In C, the difference between the two groups was tested by the Log-Rank test. In E-H, One-way ANOVA test was used to detect the difference. In I, J and K, Student's t-test in comparison with si-NC MI group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.