Figure 6.
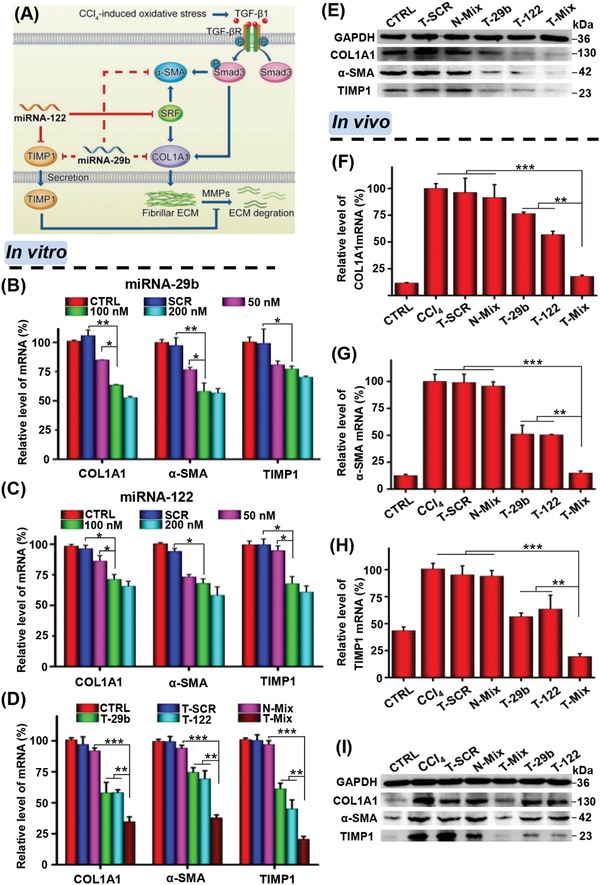
miRNA dose and synergistic effect of miRNA‐29b and miRNA‐122 on inhibition of fibrosis‐related gene expressions in vitro and in vivo. A) Schematic illustration of the synergistic antifibrosis mechanism of combined therapy with miRNA‐29b and miRNA‐122. Relative mRNA levels of COL1A1, α‐SMA, and TIMP1 in HSCs incubated with B) miRNA‐29b and C) miRNA‐122 at 0, 50, 100, and 200 × 10−9 m complexed with T‐PBP micelle. Synergistic effect of a combination of miRNA‐29b and miRNA‐122 on D) mRNA and E) protein expressions of COL1A1, α‐SMA, and TIMP1 as evaluated by real‐time PCR and Western blot. The concentration of miRNA was 100 × 10−9 m, and 50 × 10−9 m miRNA‐29b and 50 × 10−9 m miRNA‐122 were used for N‐Mix and T‐Mix groups, respectively. F–H) Relative mRNA and I) protein expressions of COL1A1, α‐SMA, and TIMP1 in the liver sliced from rats receiving different treatments. Data are shown as mean ± SD, n = 3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. Abbreviations: CTRL in parts (B)–(E), cells without treatment; T‐SCR, T‐PBP micelle complexing SCR; N‐Mix, PBP micelle complexing miRNA‐29b and miRNA‐122; T‐29b, T‐PBP micelle complexing miRNA‐29b; T‐122, T‐PBP micelle complexing miRNA‐122; T‐Mix, T‐PBP micelle complexing miRNA‐29b and miRNA‐122; CTRL in parts (F)–(I), normal rat treated with equal quantity of olive oil; CCl4, CCl4‐induced liver fibrotic rat just treated with PBS. Rats, except in the CTRL group, were pretreated with CCl4 to induce liver fibrosis.
