Figure 7.
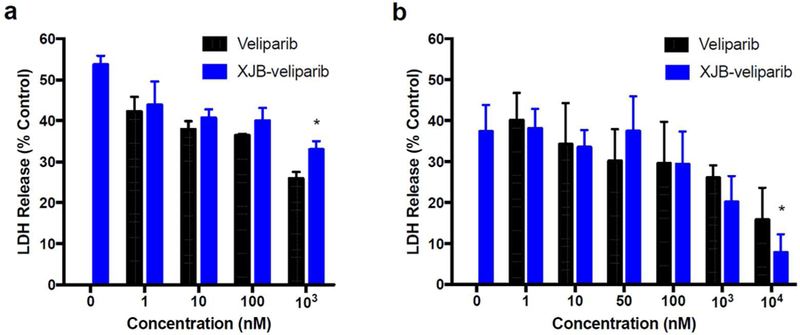
Excitiotoxicity in rat primary cortical neurons or HT22 cells treated with XJB-veliparib or veliparib.
(a) Glutamate-glycine excitotoxicity in primary cortical neurons. Neurons were exposed to 10 µM L-glutamate and 10 µM glycine, with 1–100 µM of XJB-veliparib or veliparib for 24 h (*P < 0.05 vs. veliparib, n = 6/group; mean ± SD).
(b) Glutamate excitotoxicity in an immortalized hippocampal neuronal HT22 cell line. XJB-veliparib and veliparib were both effective at inhibiting excitotoxic cell death, with XJB-veliparib slightly more effective at higher doses (*P < 0.05 vs. naked veliparib; n = 5/group; mean ± SD).
