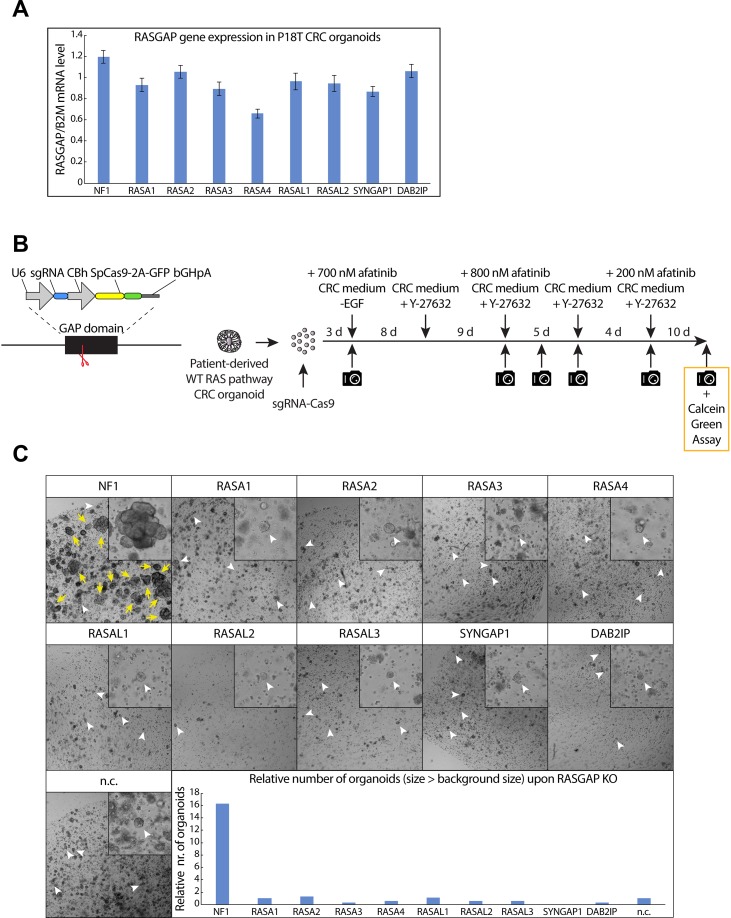
Figure 2. CRISPR screen against RASGAPs in patient-derived CRC organoids reveals increased growth and EGF-independent survival upon loss of NF1 GAP activity.
(A) The mRNA expression level of 9 RASGAPs containing an active GAP domain was analyzed in P18T organoids using qPCR. The relative expression of each RASGAP gene was normalized to the B2M housekeeping gene (representative from n = 3 independent experiments). (B) Left; schematic representation of expression plasmid containing both an U6 promoter-driven sgRNA and a CBh promoter-driven SpCas9-2A-GFP was used to target the RASGAP domain. Right; schematic overview of the RASGAP knock out screen in P18T patient-derived CRC organoids that are wild type for the RAS signaling pathway. (C) P18T CRC organoids in selection medium that have been transfected with indicated sgRNAs and Cas9. White arrow heads indicate representative background organoids. Yellow arrows indicate successful organoids that are significantly larger than background. Bar graph depicts the relative number of organoids with a size larger than background organoids as determined in the negative control. Area of alive RASGAP knock out organoids was measured using calcein green assay (see Materials and Methods).