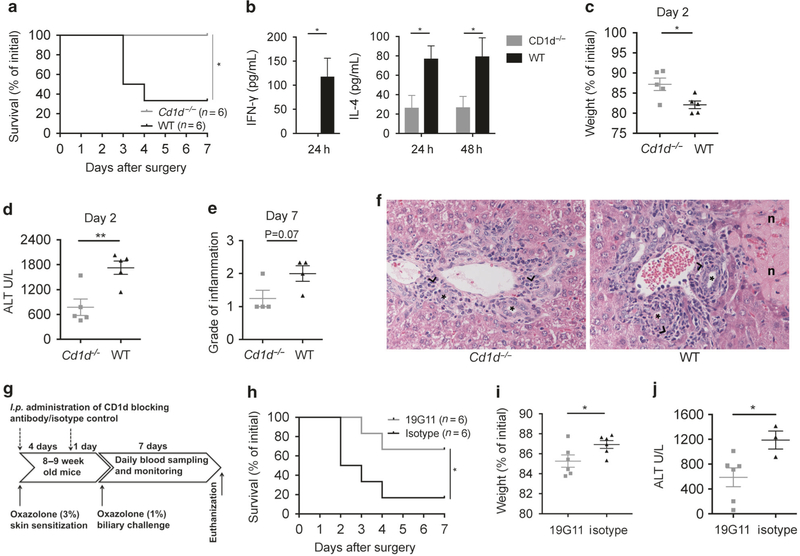
Fig. 5.
Oxazolone cholangitis is dependent upon CD1d and NKT cells. Survival curve (a) comparing Cd1d−/− and WT mice upon biliary oxazolone challenge. Bar graphs showing serum concentrations of IFN-γ and IL-4 at indicated time points after biliary oxazolone challenge in WT (n = 5) and Cd1d−/− (n = 5) mice (b). Weight loss (c), peak serum ALT levels (d) and histologic evaluation of portal inflammation (e) where the score indicates degree of pathology as either absent (0), mild (1), moderate (2) or severe (3) at the indicated days after biliary challenge with oxazolone in Cd1d−/− and WT mice. Representative H&E staining of livers (f) 7 days after biliary oxazolone challenge in the indicated mouse strains, captured in 40× magnification (asterisks: bile ducts; black arrowheads: portal inflammation; n: necrosis). Timeline (g) showing the oxazolone cholangitis model with biliary oxazolone challenge 5 days after skin sensitization and 7 days postoperative follow-up before killing, with additional i.p. injection of a CD1d-blocking antibody, 19G11 or isotype control at two time points: first at the time of skin sensitization and second the day before the surgery. Survival (h) of WT mice upon biliary oxazolone challenge and antibody blocking with either 19G11 or isotype control. Weight loss (i) at day 1 and peak serum ALT levels (j) at day 2 after oxazolone challenge in indicated mice. Each symbol represents a single mouse. Representative results from three independent experiments are shown, presented as mean±SEM. ALT alanine transaminase, H&E hematoxylin and eosin, IFN interferon, IL interleukin, WT wild type. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01