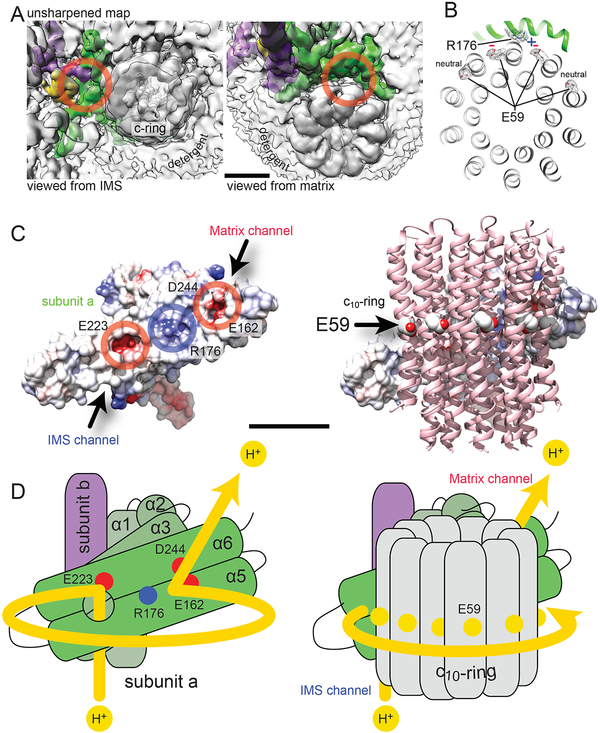
Figure 4. Proton translocation mechanism.
A, The unsharpened map reveals cavities in the complex that correspond to the IMS (left) and matrix (right) half-channels. B, The E59 residues of the two c-subunits nearest to R176 are in extended (deprotonated) conformations. The remaining E59 residues are in proton-bound conformations. C, There are two patches of negative charge on subunit a (left) where it interacts with the c-ring (right) that correspond with expected positions of the IMS and matrix half-channels. D, During proton translocation, protons follow the path indicated by the yellow line (left), entering the IMS half-channel behind transmembrane α-helices 5 and 6 of subunit a and exiting through the matrix half-channel between α-helices 5 and 6 and the c-ring (right). Scale bars, 25 Å.