Figure 6.
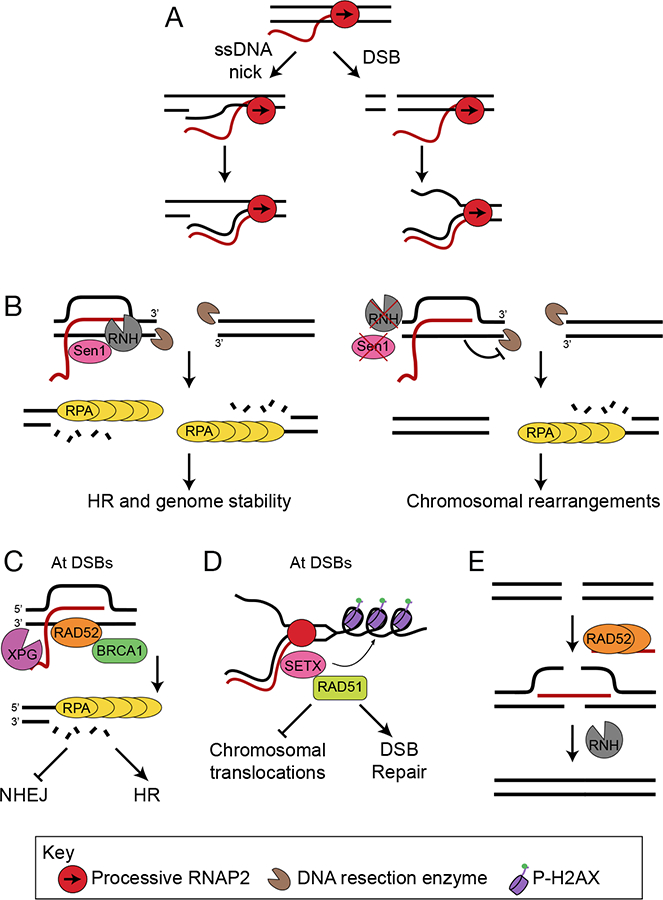
R-loops participate in DNA repair at breaks. A) DNA breaks, either ssDNA nicks (left) or DSBs (right), create free 3’-DNA ends, promoting the annealing of RNA to DNA to form hybrids. B) In yeast, R-loops form at DSBs and initiate repair by HR. Subsequent R-loop resolution by Sen1 or RNase H regulates the extent of DNA end resection and subsequent binding of RPA (left). In the absence of Sen1 or RNase H (right), RNA-DNA hybrids persist, blocking DNA resection and RPA binding and leading to chromosomal rearrangements. C) In human cells RNA-DNA hybrids formed at a subset of DSBs recruit Rad52, which further recruits XPG and BRCA1. XPG-mediated R-loop processing initiates DNA resection and repair by HR, and suppresses aberrant NHEJ. D) SETX is recruited to DSBs and resolves RNA-DNA hybrids at active genes. SETX regulates γH2AX spreading and Rad51 foci formation promoting DSB repair and suppressing chromosomal translocations. E) Rad52 promotes the formation of RNA- DNA hybrids that facilitate RNA-templated HR by bridging two DNA ends. The DNA ends are ligated, and the RNA strand is removed by RNase H.
