Fig. 3. Higher herbivore bite rates were associated with more finely cropped turfs, which would otherwise reduce the recruitment of corals to the reef.
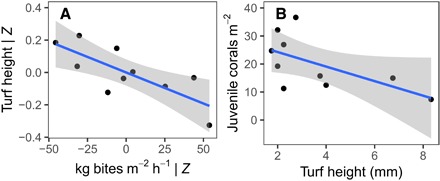
Plotted values in (A) are the partial effects of bite rate, which, having accounted for the influence of all other predictors (Z) in the multiple regression model, thus reflect the statistically independent effect of mass-standardized bite rate (kg bites per m2 per hour) on algal turf canopy height (mm) (R2 = 0.80). (B) Bivariate correlation between algal turf canopy height and the number of juvenile corals per m2 (R2 = 0.48). Fitted lines are linear regressions ± 95% confidence intervals.
