Fig. 1. HERV transcriptome profile in human breast cancer.
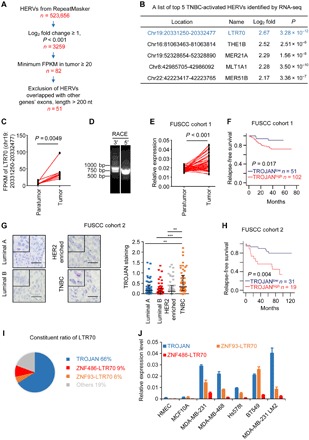
(A) Schematic diagram depicting the screening of TNBC-related HERVs. RNA-seq detected HERV expression across eight paired TNBC tissues and adjacent normal tissues for HERVs derived from RepeatMasker. FPKM, fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads. (B) The top 5 TNBC-related HERVs identified by RNA-seq. (C) The expression of LTR70 [chromosome (chr) 19: 20331250-20332477] in eight paired TNBC tissues and adjacent normal tissues. P value was determined using two-tailed paired Student’s t test. (D) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products generated in the 3′ (left) and 5′ (right) RACE assay covering the 5′ and 3′ ends of the TROJAN transcript. (E) The quantitative PCR (qPCR) analysis of the relative TROJAN transcription levels in TNBC tissues (n = 53) versus the adjacent normal breast tissues (n = 53) in FUSCC cohort 1. P value was determined using two-tailed paired Student’s t test. (F) Kaplan-Meier analysis of the relapse-free survival of 153 patients with TNBC in FUSCC cohort 1. A log-rank test was used to determine the statistical significance between the low TROJAN expression group (n = 51) and the high TROJAN expression group (n = 102). (G) RNA ISH of TROJAN in breast cancer tissues with different subtypes (n = 50 each) (FUSCC cohort 2). Scale bars, 50 μm. The data are presented as the median with interquartile range; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. (H) Kaplan-Meier analysis of the relapse-free survival of 50 patients with TNBC in FUSCC cohort 2. The log-rank test was used to determine statistical significance between the low TROJAN expression group (n = 31) and the high TROJAN expression group (n = 19). (I) The constituent ratio of LTR70. The assay was performed by RNA-seq. (J) The qPCR analysis of the expression of TROJAN and two other LTR70s in multiple cell lines. The data are presented as the mean ± SD; n = 3 independent experiments. See also figs. S1 and S2.
