Figure 5.
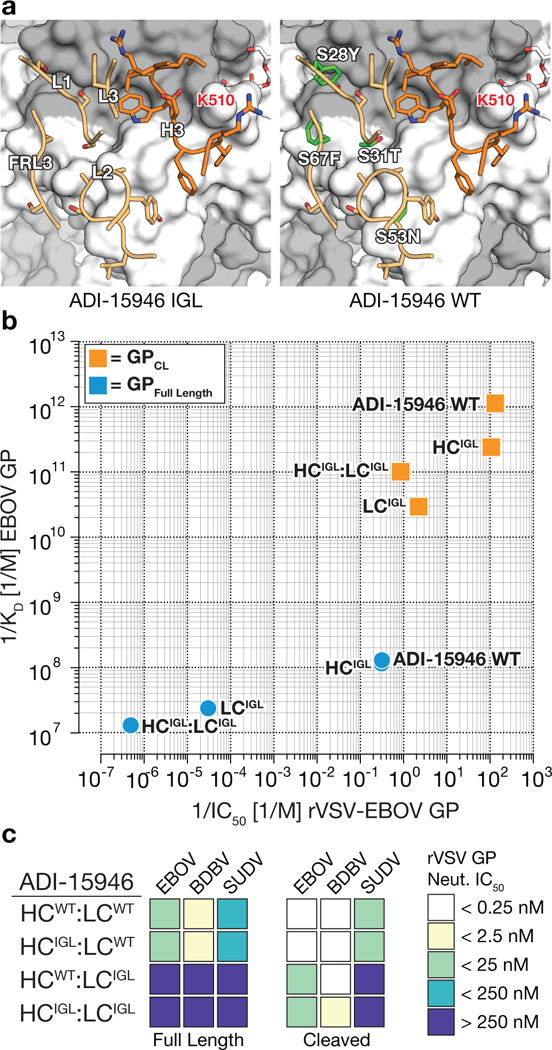
Genesis of ADI-15946. (a) Models showing differences between the ADI-15946 IGL sequence (left) and the mature antibody (WT, right). GP1 is shown in grey and GP2 in white. (b) Comparison of the apparent equilibrium dissociation constant (1/KDapp; higher value is tighter binding) for binding of ADI-15946 variants (WT, IGL, and WT:IGL chimeras) to GPCL to their capacity to neutralize rVSV-EBOV GP infection (1/IC50; higher value is more potent neutralization). (c) Heat maps for neutralization of rVSVs bearing ebolavirus GP and GPCL proteins by the indicated ADI-15946 variants.
