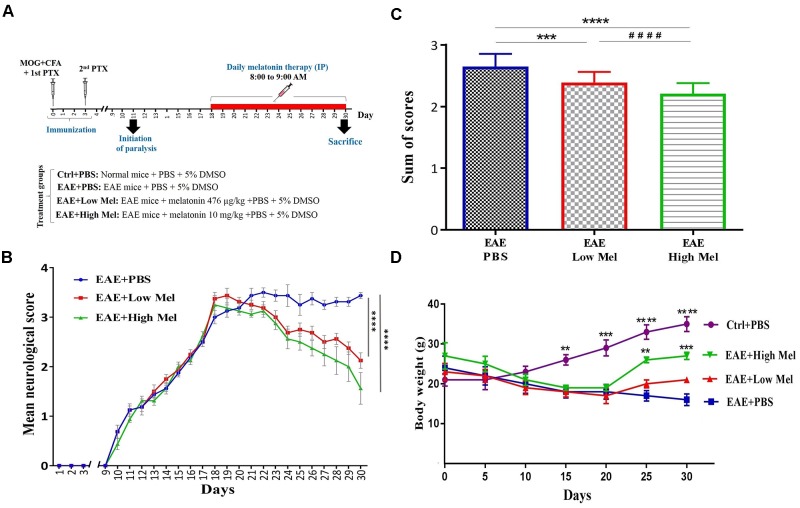
FIGURE 1.
Melatonin ameliorates the clinical scores of EAE. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental procedures. EAE was induced in C57BL6 mice (day 0) which were treated at day 18 with PBS, low or high doses of melatonin until day 29. Daily clinical scores were then measured, which continued until day 30. (B) Neurological disability analysis displayed an amelioration in EAE disease severity in melatonin treated mice compared to PBS treated EAE mice. (C) Cumulative neurological disability was significantly lower in mice treated with physiological (476 μg/kg/day) or pharmacological (10 mg/kg/day) doses of melatonin, compared to PBS treated EAE mice. (D) The mean body weight was recorded at 5 days interval. Melatonin treated mice significantly gained body weight at days 25 and 30, in comparison to vehicle. Values are expressed as the Mean ± SEM. Each group included 8 mice (n = 8). Statistical analysis was performed by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s test. Significance is indicated by ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 vs. vehicle and ####p < 0.0001 vs. EAE-low melatonin.