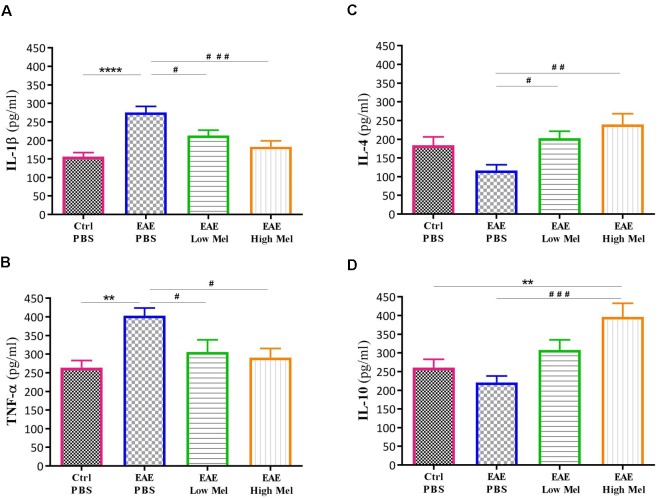
FIGURE 2.
Effect of melatonin on cytokine levels in brain, using ELISA. Levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (A) IL-1β and (B) TNF-α. Melatonin significantly suppressed their release. Levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines (C) IL-4 and (D) IL-10. Melatonin significantly increased the levels of IL-4 and IL-10. Values are expressed as the Mean ± SEM. Each group included 8 mice (n = 8). Statistical analysis was performed by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s test. Significance is indicated by ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 vs. control-PBS and #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, and ###p < 0.001 vs. EAE-PBS.