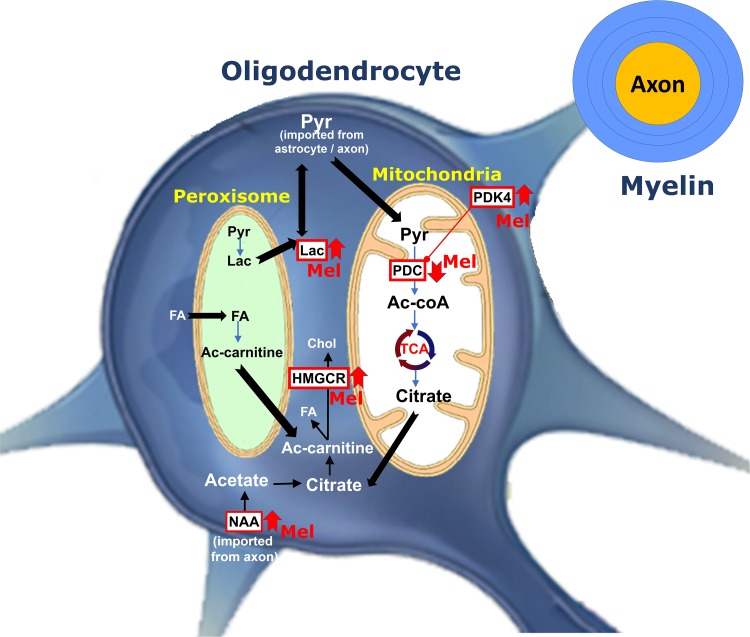
FIGURE 8.
Schematic representation for the role of melatonin on oligodendrocyte metabolism during remyelination. Pyruvate imported into myelin is converted within mitochondria by PDC to produce acetyl-CoA, which generates citrate by TCA. Citrate is subsequently used to produce fatty acid (FA) and cholesterol in the cytosol. PDK4 acts as one of the regulators of PDC activity. Melatonin increases PDK4 expression levels and cause suppression of PDC by its phosphorylation. This results into pyruvate being transferred to peroxisome where FA breakdown occurs to provide redox balance and acetyl-CoA. On the other hand, melatonin increases the levels of NAA. Axonal NAAs are transferred into oligodendrocytes and are converted to acetate and then acetyl-CoA, a substrate for FA and cholesterol synthesis. Finally, melatonin upregulates the expression of HMGCR, a key factor in cholesterol synthesis. (PDC, Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; PDK4, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases 4; Ac-CoA, Acetyl-CoA; Ac-carnitine, Acetyl-carnitine; HMGCR, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A reductase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; Chol, Cholesterol; Pyr, Pyruvate; NAA, N-acetylaspartate, Lac, lactate, FA, Fatty acid, Mel, melatonin).