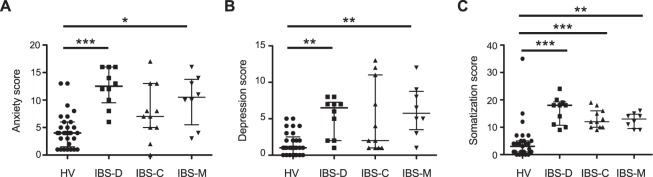
Figure 3.
Psychological scores in IBS patients and HV. Anxiety and depression scores were assessed using the anxiety and depression components of the HADS score, while somatization was assessed using the PHQ-15 score. The anxiety (A) (HV: 4.0 [1.5–6.0], n = 29; IBS-D: 12.5 [9.5–16.0], n = 10; IBS-C: 7.0 [5.0–13.0], n = 11; IBS-M: 10.5 [5.5–13.8], n = 8; Kruskal Wallis Test p < 0.0001; HV vs. IBS-D p < 0.001, HV vs. IBS-M p < 0.05) and depression (B) (HV: 1.0 [0–2.5], n = 29; IBS-D: 6.5 [2.0–7.3], n = 10; IBS-C: 2.0 [1.0–11.0], n = 11; IBS-M: 5/8 [3.5–8.8], n = 8; Kruskal Wallis Test p < 0.0001; HV vs. IBS-D p < 0.01, HV vs. IBS-M p < 0.01) scores for both IBS-D and IBS-M patients were significantly different from HV; no differences between subgroups was noted. Similarly, while all IBS subtypes exhibited increased somatization scores when compared to HV (C) (HV: 3.0 [1.0–5.0], n = 29; IBS-D: 18.0 [10.8–19.3], n = 10; IBS-C: 12.0 [10.0–16.0], n = 11; IBS-M: 13.0 [9.5–14.8], n = 8; Kruskal Wallis Test p < 0.0001; HV vs. IBS-D p < 0.001, HV vs. IBS-C p < 0.001, HV vs. IBS-M p < 0.01), no differences between subgroups were noted.