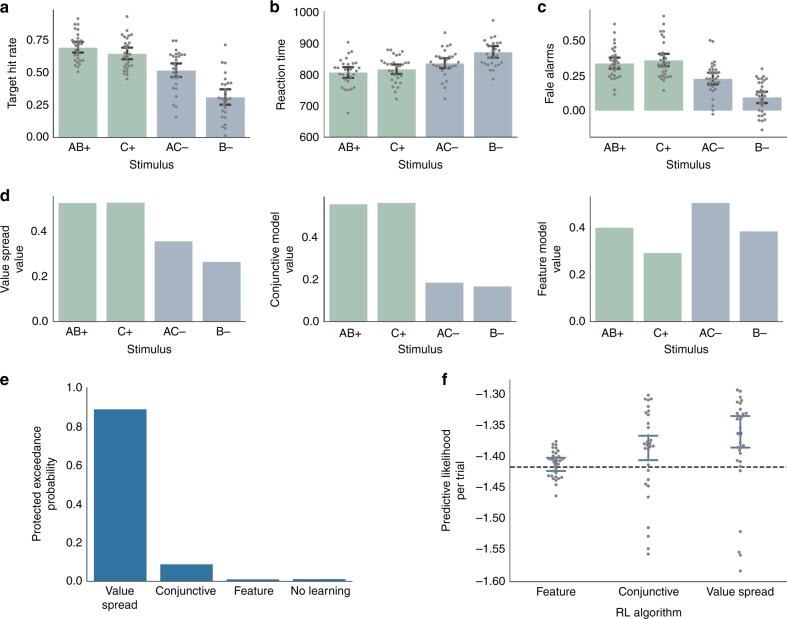
Fig. 2.
Behavior and modeling results. a Proportion of target trials in which the subject responded quickly enough to the target to earn a reward. Stimuli that were associated with the target (AB+, C+; green) had a higher hit rate than those that were not (AC−, B−; blue). In addition, stimuli with single features (C+, B−) were associated with a lower hit rate than those with two features (AB+, AC−). Further, this feature effect interacted with the target outcome effect. b Reaction times for each of the stimulus types. Reaction times were faster for stimuli associated with a target. The use of an adaptive RT threshold caused smaller differences in reaction times among conditions to translate into larger differences in hit rates in a. c False alarms for each stimulus type. Subjects were more likely to respond when no target occurred for stimuli that were associated with the target. d Value estimates from the value spread, conjunctive, and feature models. The conjunctive model showed an effect of target, such that AB+ and C+ had a higher value than B− and AC−. The feature model showed an effect of features, such that AB+ and AC− had a higher value than B+ and C−. Only the value spread model showed both the effect of target and the interaction between target and the number of features (present in a–c). e Bayesian random effects model comparison showed the Value Spread RL model most likely accounted for behavior. The protected exceedance probabilities summed to 1 across the models, and because they express a group random-effects measure, there are no error bars. f The cross-validation model comparison showed the Value Spread RL model best predicted unseen data. Log predictive likelihoods closer to 0 indicate better performance. Likelihoods are expressed per trial to normalize across differences in the number of responses among subjects. The dashed black line indicates the performance of the null model. Error bars for all panels depict bootstrapped estimates of the standard error of the group mean