Fig. 3.
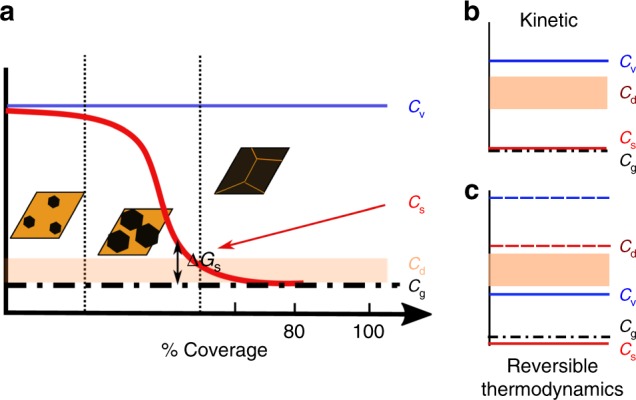
Schematic of growth thermodynamics and kinetics. a Carbon potentials at various coverage levels with reference to that inside the graphene grain Cg. Cd, Cs, and Cv represent defect (at grain boundary), surface and vapor phase potentials. b Energetic situation in which the lack of grain boundary closure will be termed kinetic. Vapor carbon potentials are greater than those at the defect levels and thus closure is not impeded by global thermodynamics. However, local (in the vicinity of the grain boundary being formed) surface potentials determined by adsorption-desorption kinetics can be lower than the defect potential thus preventing closure. c Energetic situation in which the lack of grain boundary closure is thermodynamic. Those grain boundary structures in which the carbon potentials are higher than Cv cannot be formed. Raising carbon potentials will form these structures, as shown by dotted lines, whereas lowering it will remove carbon from these locations leaving behind vacant sites
