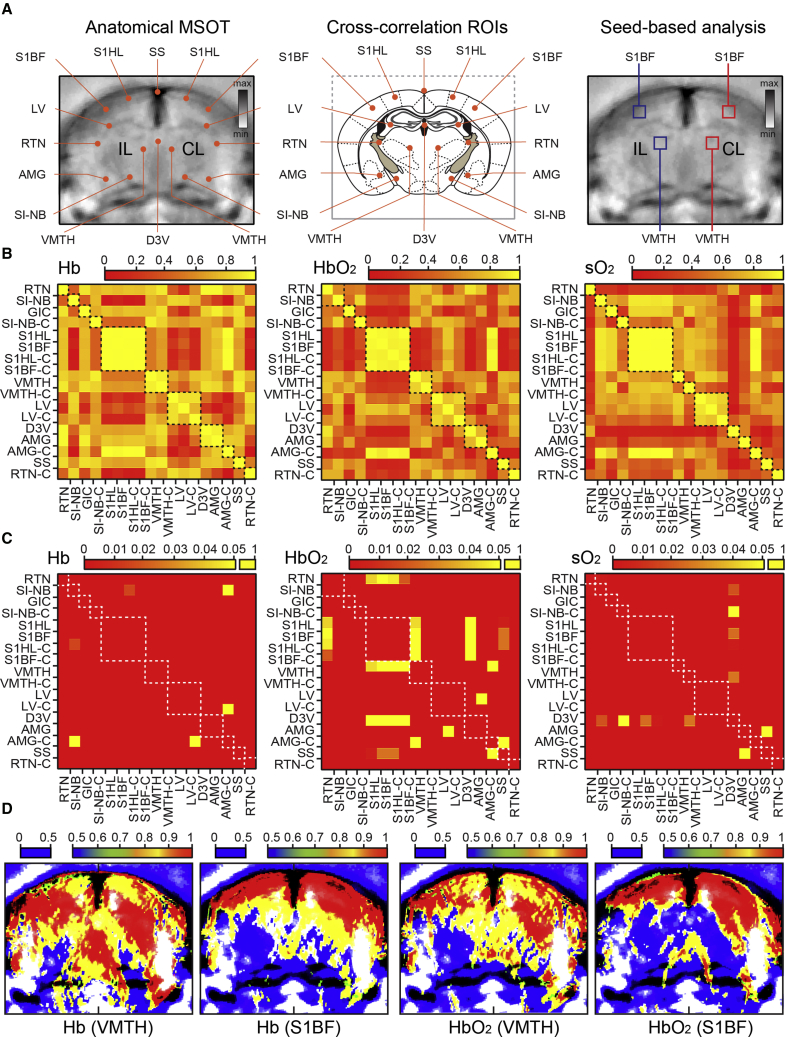
Figure 3.
Temporal Coherence of Hemodynamic Changes Induced by Stimulation of Whisker Inputs in Mouse Brain
(A) Structural MSOT images (left and right panels) with marked ROIs used in cross-correlation analysis (left) and in seed-based correlation mapping the functional connectome (right), along with schematized map of corresponding brain plane with anatomical references (middle). For abbreviations, see Figure 2 legend.
(B and C) Correlation matrix of Hb, HbO2, and SO2 illustrating the degree of temporal coherence of hemodynamic response induced by whisker inputs (B) and corresponding graph of the distribution of p values of same ROIs (C).
(D) Seed-based correlation maps of the same brain illustrating areas with temporally coherent changes in Hb and HbO2 signals (i.e., co-activation) in response to whisker inputs. Whisker input driven changes of the hemodynamic signals in the contralateral somatosensory cortex barrel field (S1BF) and contralateral ventro-medial thalamic nucleus (VMTH) have been used as seeds for current coherence maps, with the degree of correlation presented in the color bars.