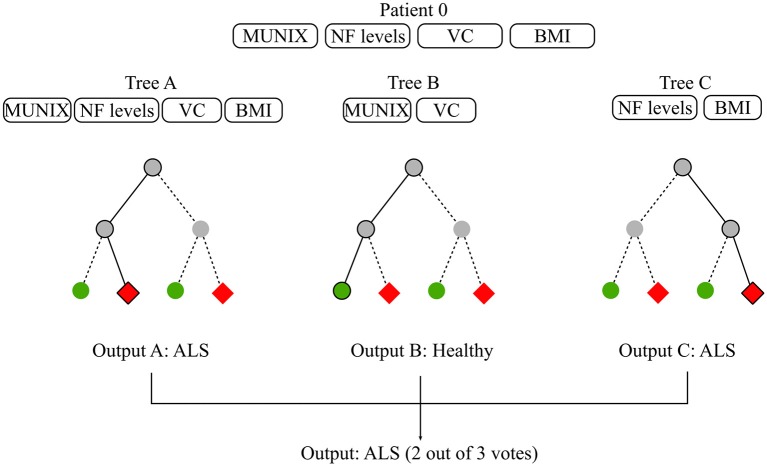
Figure 4.
Random forest for diagnosis. The available data consist of basic biomarkers features which are MUNIX, CSF Neurofilament (NF) levels, Vital Capacity (VC), and BMI. The objective is to classify subjects between healthy and ALS patients. The RF contains 3 decisions trees which use different feature subsets to learn a diagnosis model. Tree A learns on all available features, Tree B learns on MUNIX and VC, Tree C learns on NF levels and BMI. Each tree proposes a diagnosis. RF diagnosis is computed based on the majority vote of each of the trees contained in the forest. Given that two out of three trees concluded that patient 0 had ALS, the final diagnosis suggested by the model is ALS.