-
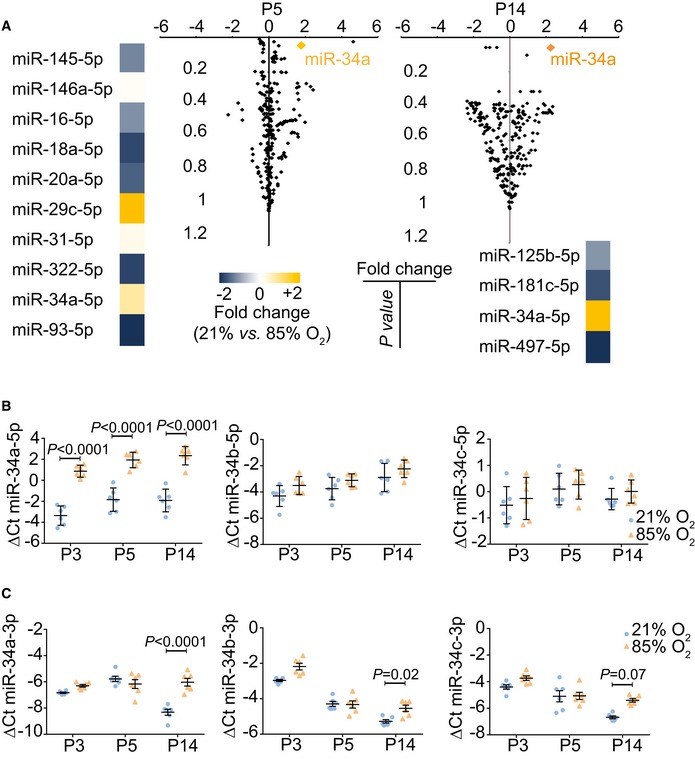
A
Microarray analysis of microRNA expression changes in newborn mouse lungs exposed to 21% O
2 versus 85% O
2, at post‐natal day (P)5 and P14. Microarray data are available at the GEO database under accession number
GSE89666.
-
B
Quantitative RT–PCR detection of microRNA‐34a/b/c‐5p family members in the lung over the course of normal (21% O2) and aberrant (85% O2) alveolarization.
-
C
Quantitative RT–PCR detection of microRNA‐34a/b/c‐3p family members in the lung over the course of normal (21% O2) and aberrant (85% O2) alveolarization.
Data information: For (A), a Welch's approximate
t‐test was employed to determine
P values (
n = 4 animals for each experimental group), which were corrected using the algorithm of Benjamini and Hochberg, as described in the Materials and Methods under the heading “Power and statistical analyses”. For (B) and (C), data represent mean ± SD (
n = 6 animals for each experimental group).
P values were determined by one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's
post hoc modification, and all
P values < 0.05 for 21% O
2 versus 85% O
2 comparisons at each developmental stage (P3, P15, and P14) are indicated.