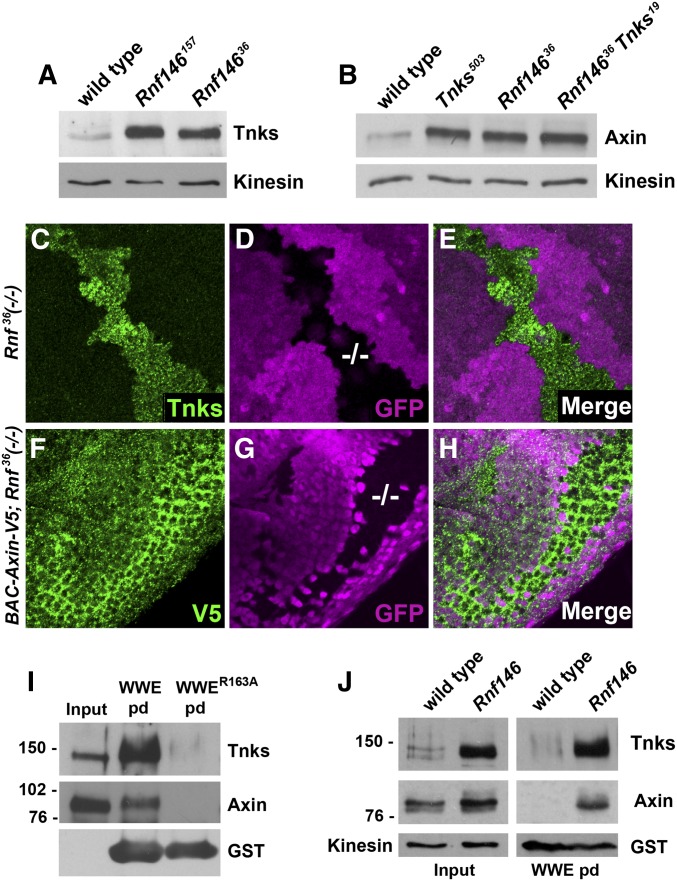
Figure 2.
Drosophila Rnf146 mediates ADP-ribose-directed destabilization of Axin and Tnks in vivo. (A) Immunoblot of lysates from wild-type and Rnf146 null mutant larvae probed with Tnks and Axin antibody. Tnks and Axin protein levels are increased in Rnf146 mutant larvae. Kinesin was used as a loading control. (B) Immunoblot of lysates from wild type, Tnks null mutant, Rnf146 null mutant, and Rnf146 Tnks double null mutant larvae probed with Axin antibody. Axin protein levels are increased in Tnks and Rnf146 mutants, but not further increased in Rnf146 Tnks double mutants. Kinesin was used as a loading control. (C–E) Third-instar larval wing imaginal discs with Rnf14636 null mutant clones marked by the absence of GFP (−/−; magenta) were stained with indicated antibodies. Tnks accumulates cell autonomously in Rnf14636 mutant clones. (F–H) Eye imaginal discs from third-instar larvae expressing a BAC Axin-V5 transgene with Rnf146 null mutant clones were stained with indicated antibodies. Rnf146 mutant clones were marked by the absence of GFP (−/−; magenta). (I) Detection of poly-ADP-ribosylated Tnks and ADP-ribosylated Axin using the GST-WWE pulldown assay. (J) poly-ADP-ribosylated Tnks and poly-ADP-ribosylated Axin accumulated in Rnf146 null mutants.