Table 1.
Catalyst screening and optimization of reaction conditionsa.
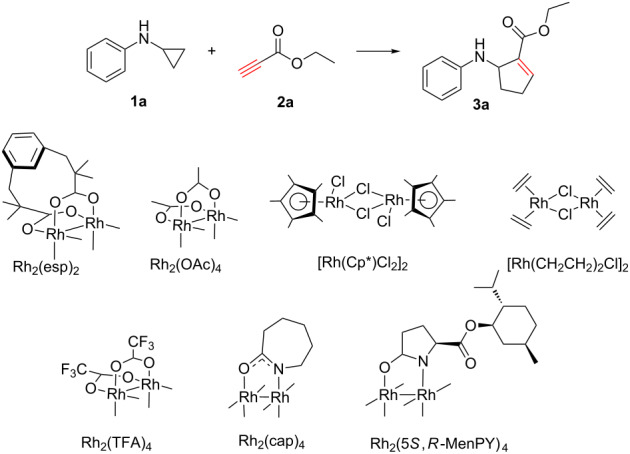 | |||
| Entry | Conditions | Solvent | Yieldb (%) |
| 1 | no catalyst | DCM | NR |
| 2 | [Rh(CH2CH2)2Cl]2 | DCM | ND |
| 3 | [Rh(Cp*)Cl2]2 | DCM | 72 |
| 4 | Rh2(OAc)4 | DCM | 45 |
| 5 | Rh2(TFA)4 | DCM | 52 |
| 6 | Rh2(esp)2 | DCM | 68 |
| 7 | Rh2(cap)4 | DCM | 40 |
| 8 | Rh2(5S,R-MenPY)4 | DCM | 61 |
| 9c | Rh2(esp)2 | DCM | 39 |
| 10c | [Rh(Cp*)Cl2]2 | DCM | 44 |
| 11c | Rh2(5S,R-MenPY)4 | DCM | 58 |
| 12c | Rh2(5S,R-MenPY)4 | DCE | 67 |
| 13c | Rh2(5S,R-MenPY)4 | hexane | 59 |
| 14c | Rh2(5S,R-MenPY)4 | toluene | 59 |
| 15c | Rh2(5S,R-MenPY)4 | DME | 60 |
| 16c | Rh2(5S,R-MenPY)4 | DMF | 33 |
aReaction conditions: 1a (0.5 mmol, 0.2 M in degassed solvent), 2a (2.5 mmol), catalyst (1 mol %) under argon at room temperature for 24 h unless otherwise noted. bIsolated yield. c0.1 mol % of catalyst. esp = α,α,α’,α’-tetramethyl-1,3-benzenedipropionate, cap = caprolactamate, 5S,R-MenPY = (S)-(1R,2S,5R)-2-isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexyl 2-oxopyrrolidine-5-carboxylate, NR = no reaction, ND = not detected.
