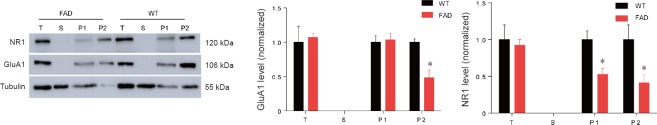
Figure 5.
Decreased subcellular distribution of glutamate receptors in the hippocampus of 5XFAD mice at 10 weeks old.
(A) Western blots showing the expression of glutamate receptors in different subcellular fractions in the hippocampus from wild-type and 5XFAD mice at 10 weeks of age. The α-tubulin was considered the internal control to normalize total protein level. (B) Normalization of AMPA-selective glutamate receptor 1 (GluA1) in different subcellular fractions in the hippocampus from 10-week-old WT and 5XFAD mice. (C) Normalization of NMDA receptor 1 (NR1) in different subcellular fractions in the hippocampus from 10-week-old WT and 5XFAD mice. *P < 0.05, vs. WT (mean ± SEM; n = 3 mice/genotype for GluA1, n = 4 mice/genotype for NR1; Student’s t-test). T: Total protein in tissue; S: cytosolic fraction; P1: triton-soluble fraction in the crude synaptosome fraction, which mainly includes cytosolic proteins in synapses; P2: triton-insoluble fraction in the crude synaptosome fraction, which mainly includes membrane-associated proteins in synapses. WT: Wild-type; FAD: family Alzheimer’s disease; AMPA: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid; NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartic acid.