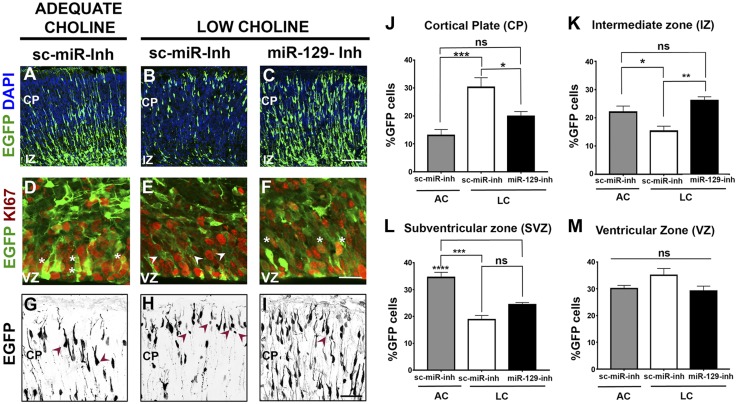
Figure 4.
Inhibition of miR-129-5p function in NPCs restores neurogenesis in the LC E17 cortex. A) In AC embryos transfected with sc-miR-inh, EGFP-labeled cells were found in the VZ and SVZ and migrating toward the CP. B) EGFP-labeled cells in LC cortex were consistently fewer in number vs. the AC cortex and were primarily located in the VZ and the CP. C) Electroporation of LC cortex with miR-129-5p inhibitor restored the distribution of EGFP-labeled cells across the different layers of the cerebral wall and increased their number. D–F) Expression of EGFP and the proliferative cell marker Ki67 in the VZ/SVZ of transfected embryonic cortices. EGFP (D) was coexpressed with Ki67 in cells electroporated with sc-miR-inh (asterisks). VZ of LC embryos (E) contained many EGFP+ cells that did not express Ki67 (arrowheads). Most EGFP+ cells (F) electroporated with miR-129-inh in LC embryos expressed Ki67 (asterisks). G) AC pyramidal neurons transfected with sc-miR-inh exhibit typical morphology of immature pyramidal neurons (arrowheads). H) EGFP-expressing cells in the CP of LC embryos displayed a small cell body size and abnormal morphology (arrowheads). I) Transfection of LC NPCs with miR-129-5p inhibitor improves differentiating pyramidal cell morphology (arrowhead). J–M) Comparison of proportions of EGFP-expressing cells in the cortical walls of LC embryos transfected with sc-miR-inh and LC embryos transfected with miR-129-inh (n = 4 per group) demonstrated increased proportions of labeled cells in the CP (J) and reduced proportions of cells located in the IZ (K) and the SVZ (L), compared with AC embryos transfected with sc-miR-inh. Inhibition of miR-129-5p function in LC cortices decreased the proportion of cells occupying the CP (J) and increased the proportions of cells occupying the IZ (K). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 by 1-way ANOVA test. At least 3 embryos per condition were analyzed. Scale bars: 100 μm(C); 35 μm (F); 50 μm (I).