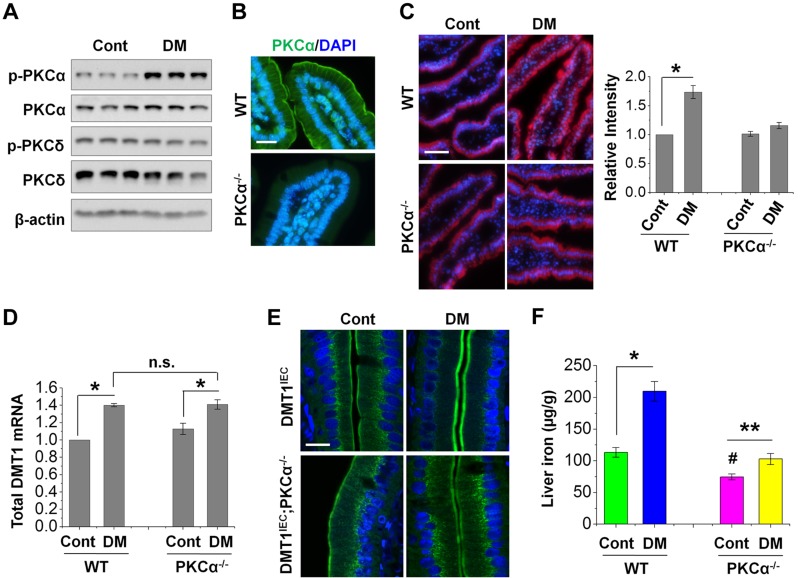
Figure 4.
PKCα mediates increased membrane DMT1 expression and iron uptake in diabetic mice. A) The expression of total and phosphorylated (p) form of PKCα and PKCδ in control (Cont) and diabetic (DM) mouse duodena was determined by immunoblotting with the corresponding antibodies. B) PKCα localization in IECs was determined by microscopic analysis using PKCα−/− mice as a negative control. Scale bar, 10 μm. C) Representative images show the labeling of Fe2+ by RhoNox-1 (5 µM) in duodenal epithelium of WT and PKCα−/− mice. The fluorescent intensity was quantified from 6 villi of each mouse (n = 5 mice/group), and the relative changes are shown on the right with the values of the WT-Cont mice set at 1. Scale bar, 50 μm. D) Total DMT1 mRNA expression in WT and PKCα−/− mouse duodenum was determined by qRT-PCR. Data are shown as means ± se (n = 6). E) Representative confocal images show the localization of HA-DMT1 in DMT1IEC and DMT1IEC;PKCα−/− mice as stained by anti-HA antibody. n = 5. Scale bar, 10 μm. F) Nonheme iron content was determined in the liver of WT and PKCα−/− mice with or without diabetes. Data are means ± se (n = 5). *P < 0.01, **P < 0.05, #P < 0.01 compared with the WT-Cont; N.s., not significant.