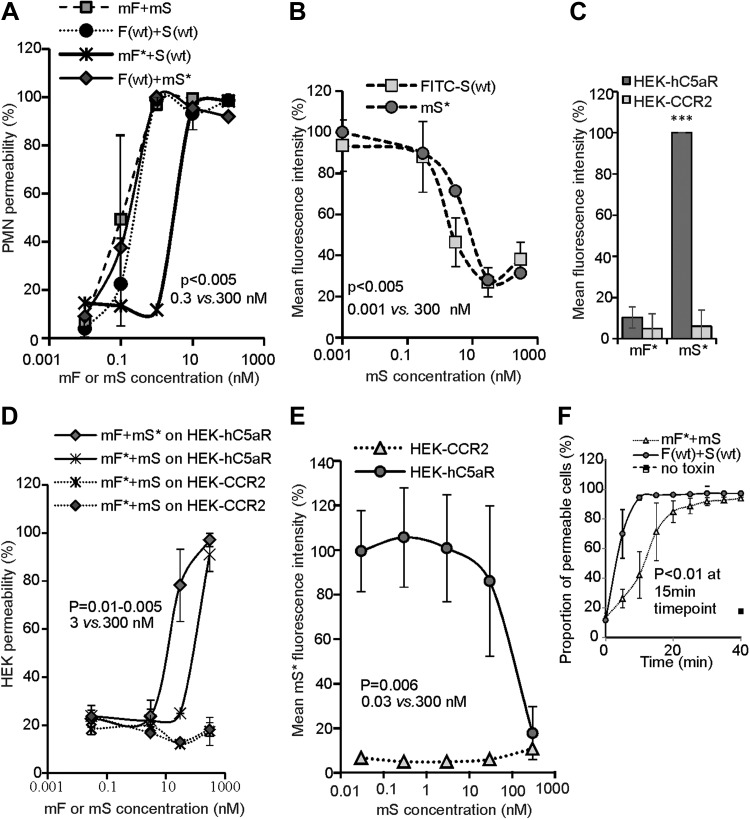
Figure 1.
Toxin functionality on PMN and HEK cells. A) PMN cell permeability in the presence of unlabeled LukSK281CY113H and LukFK288C (mS + mF; number of biologic replicates, n = 2), Alexa Fluor mS* or mF*, and F(wt) or S(wt) (n = 1), compared with PMN cell permeability of S(wt) and F(wt) (n = 3). B) Inhibition of 3 µg/ml FITC-labeled FITC-S(wt) (n = 3) and mS* (n = 1) binding to PMN cell by mS. Permeability dose dependencies for A and B are shown with a polynomial spline fit; statistical significance indicated between low (0.3 and 0.001 nM) and high (300 nM) toxin concentrations using Student’s t test. Error bars indicate sd. C) Column indicating binding responses for mF* on hC5aR cells (n = 2). ***P < 0.001, statistically significant difference between mS* binding on HEK-hC5aR cells compared with HEK-CCR2 and mF* binding on these cells. D) Permeability of hC5aR-transfected HEK cells using unlabeled mS and mF and Alexa Fluor mS* and mF* compared with S(wt) and F(wt) (n = 2). E) Inhibition of 3 µg/ml mS* binding by mS on HEK-hC5aR cells (n = 3). CCR2-transfected HEK cells used as negative controls for toxin binding and lysis in C and D (n = 2) or 1 representative experiment in C. Dose dependency shown with polynomial spline fit. Statistical significance calculated between low (0.3 and 0.001 nM) and high (300 nM) toxin concentrations using Student’s t test. F) Permeability response of hC5aR-transfected HEK cells following incubation with unlabeled mS and Alexa Fluor maleimide mF* or toxins F(wt) and S(wt) (n = 3). Statistical significance calculated between 15 and 0 min time points using Student’s t test. Error bars indicate sd. Percentages of mean fluorescence intensity are shown as relative to the maximum intensity in each individual experiment (B, C, E). Permeability of the cells was analyzed after 30 min incubation at +37°C, whereas the inhibition assays were analyzed after 45 min incubation at +4°C (Supplemental Movie S3).