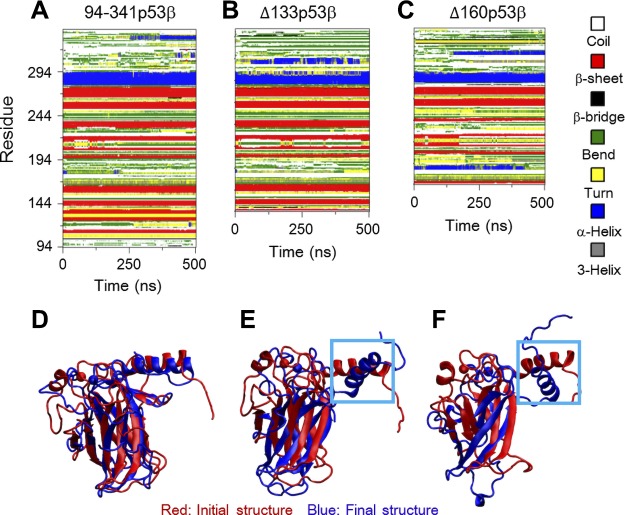
Figure 2.
A–C) The changes in the secondary structures are responsible for the larger structural fluctuations following deletions of the core domains residues, evidenced by the time evolution of secondary structure profiles. D–F) The superposed core domain structures of the final conformations (blue) of 94-341p53β (D), Δ133p53β (E), and Δ160p53β (F) with respect to their initial structure (red) revealed a larger deviation of DNA-binding motif helix H2.