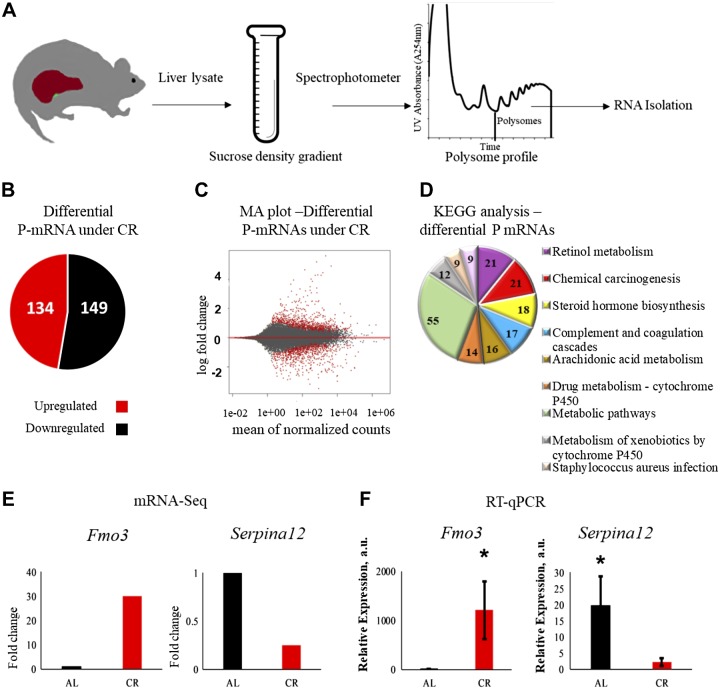
Figure 1.
CR mediated differential translation in the liver. A) The experimental workflow. Mouse liver lysates were subjected to fractionation using sucrose gradient. Total RNA was extracted from polysome fractions and mRNA-seq was performed. B) The effect of CR on the P-mRNA abundance. P-mRNAs, whose abundance was increased (red), and P-mRNAs, whose abundance were decreased (black), in the liver polysomes in response to CR. C) Log ratio/mean average (MA plot) of log-fold change for mean of normalized read counts, every dot represents individual gene, gene for P-mRNAs with differential abundance between AL and CR samples are shown by red dots. D) Enriched pathways for P-mRNAs differentially abundant under CR treatment. Pathways were sorted in decreasing order of significance. Values on the pie chart represent the number of the P-mRNAs involved in the pathways. Cutoff value was set to P ≤ 0.01. E, F) Validation of mRNA-seq data: mRNA-seq data for Fmo3 and Serpina12 (n = 12) (E) and real-time quantitative PCR on RNA extracted from polysomal fraction for Fmo3 and Serpina12 (n = 12) (F). *P < 0.05.