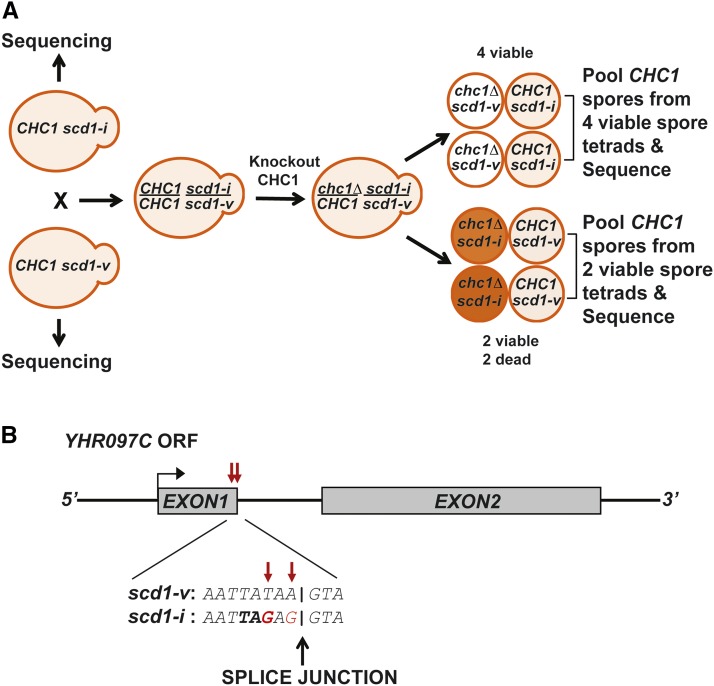
Figure 1.
Identification of SCD1 locus by next generation sequencing (NGS). (A) CHC1 strains with the scd1-v (BJ2738) and scd1-i allele (BJ2700) were crossed to each other. CHC1 was deleted from the resulting heterozygous (scd1-i/scd1-v) diploid (BJ3068). Tetrads were dissected and wild type spores were selected from tetrads with 4 viable spores (CHC1 scd1-i) or 2 viable spores (CHC1 scd1-v). Parents of the original diploid and pools of 10 CHC1 spore segregants of scd1-i or scd1-v genotype were sequenced. (B) Schematic representation of YHR097C. Exon1 and Exon2 are shown as dark gray boxes. The red arrows indicate the mutation(s), where the first mutation leads to a Tyr residue to Stop codon at codon 41 of the scd1-i allele just upstream of the 5′ splice junction.