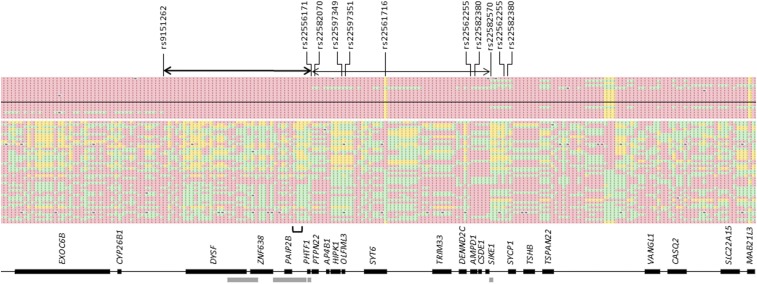
Figure 2.
Homozygosity within the region of significant SNVs, CanFam3.1 17:49,879,074-53,632,785. Each row is a DNA sample and each column shows a variant. Only variants that were segregating in this population are shown. Red and yellow indicate homozygosity for the two alleles and green shows heterozygosity. The upper block shows animals with severe goniodysgenesis (above black line) and glaucoma (below black line); the lower block shows those passed as clinically unaffected at gonioscopy testing. The most significant SNV rs22561716 is yellow in the cases (homozygous for the risk-associated allele); one clinically unaffected animal was homozygous for this allele and one severely affected animal was heterozygous. SNVs rs9151262 and rs22582070 flank the block of homozygosity (heavy black arrow). rs22582070 and rs22582570 flank a second block where all cases except one were homozygous (light black arrow). SNV rs22556171 indicates the point at which the genotypes of full siblings BC6108 (affected) and BC6113 (unaffected) become the same. Genes underlying the SNVs are indicated by black bars; the relative proportions are different from Figure 1 reflecting the differing density of markers across the region. There were no segregating markers for RSBN1, BCL2L15, DCLRE1B, BCAS2, CDK2AP1, NRAS, ENSCAFG00000009671, NGF or NHLH2. SNVs rs22597349 and rs22597351 flank the OLFML3 gene. SNVs rs22562255 and rs22582380 flank the CDK2AP1 gene. SNVs rs22562255 and rs22582380 flank ENSCAFG00000009671. Gray bars show known large structural variants and the bracket indicates the location of the break in synteny between dog and other mammals.