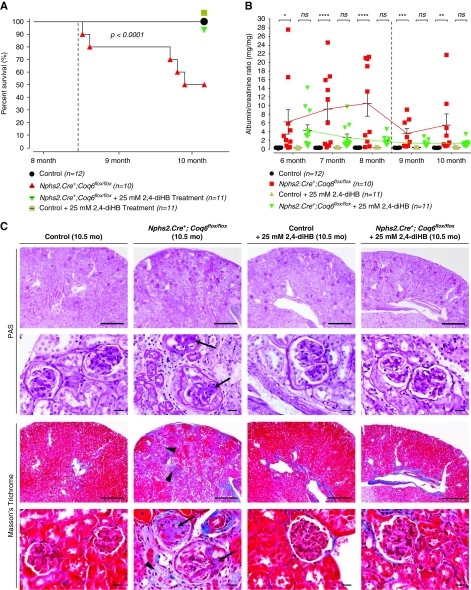
Figure 1.
Nphs2.Cre+;Coq6flox/flox mice develop severe progressive proteinuria and consecutive death in adulthood. Treatment with 2,4-diHB prevents disease progression, resulting in normal survival range. (A) Nphs2.Cre+;Coq6flox/flox mutant mice exhibit reduced life span with a median survival of 306 days, whereas Nphs2.Cre+;Coq6flox/flox mutant mice under treatment with 2,4-diHB have similar survival to healthy and healthy treated littermate controls. Dotted line displays onset of renal failure. n=10–12 animals in each group. Log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test, P<0.001. (B) Urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio serial analysis at indicated ages and genotypes (n=10–12 animals in each group) reveals progressive proteinuria in Nphs2.Cre+;Coq6flox/flox mutant mice (red square) but not in littermate controls (black circle). Nphs2.Cre+;Coq6flox/flox mutant mice under treatment with 2,4-diHB (green triangles) are protected from developing proteinuria. Dotted line displays onset of renal failure. Note that once chronic renal failure ensues, urinary albumin excretion is reduced as is known to occur in SRNS. One-way ANOVA P values, calculated using Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, are shown in the figure; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.001; each data point represents mean value of technical duplicates, error bars represent SEM. (C) Kidney serial sections and representative images of 10.5-month-old mice with indicated genotypes were stained according to indicated conditions. The Nphs2.Cre+;Coq6flox/flox mutant mice exhibit FSGS (arrows) with focal interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy (arrow heads), and proteinaceous casts in dilated tubules (asterisks). In contrast, wild-type littermate control mice and Nphs2.Cre+;Coq6flox/flox mutant mice under treatment with 2,4-diHB display normal histologic kidney morphology. Scale bars, upper rows 500 μm and lower rows 20 μm. PAS, periodic acid–Schiff.