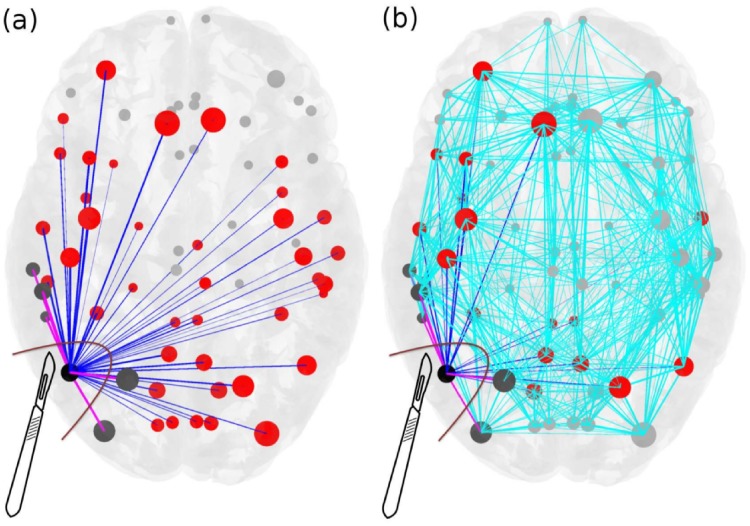
Fig 2. Scheme for comparison of standard resection methods, where the entire epileptogenic zone (EZ) is removed during surgical operation, versus lesioning minimal number of links.
Panel (a): The connectivity matrix is illustrated for an epileptogenic brain with the EZ consisting of one area (black). The outgoing connections of the EZ are blue and pink, connecting red and dark grey areas respectively, and they are all removed during the current surgical procedures of disconnecting the EZ. Targeted lesioning depicts the minimal number of links that are sufficient to be removed (pink) in order to stop the seizure, versus the total number of outgoing links from the EZs (blue) that are removed during the resection of an entire EZ. Light blue links added in panel (b) represent the full connectivity of the network. The size of the nodes reflects how strongly they are connected, and the width of the links correspond to their weight. Unaffected nodes by any of the resection procedures are light grey and unaffected links are light blue.