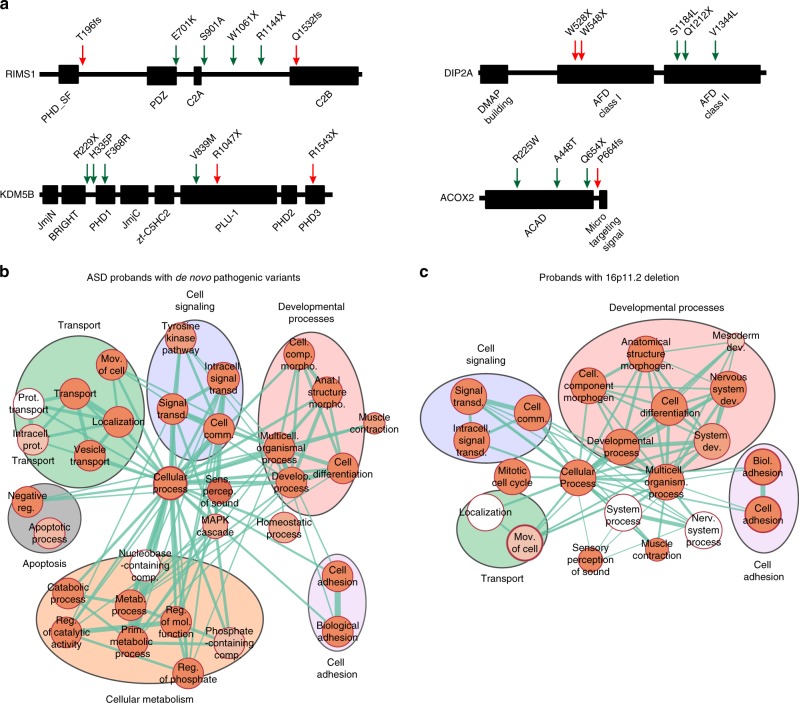
Fig. 5.
Rare variants in the genetic background affect core biological processes and disease-associated genes. (a) Examples of nonspecificity in the location of other hits in protein domains compared with first-hits. Location of variants in the protein sequences of RIMS1, DIP2A, KDM5B and ACOX2, genes with other hits (green arrows) and previously reported de novo disruptive variants in simplex autism cases (red arrows). Genes with other hits found in (b) autism spectrum disorder (ASD) probands carrying de novo disruptive variants (Simons Simplex Cohort; SSC) and (c) probands with the 16p11.2 deletion (Simons Variation in Individuals Project; SVIP) are enriched in core biological processes (FDR <0.05 with Bonferroni correction). Clusters of enriched Gene Ontology (GO) terms for “developmental processes,” “cell signaling,” “cell adhesion,” and “transport” functions are present among other hits found in each cohort. The size of each circle represents the number of genes annotated for each GO term; red shading of each circle represents the FDR for enrichment of each GO term among genes with other hits, with darker shades indicating a lower FDR. Line thickness represents the number of shared genes between pairs of GO terms. FDR values of the enriched GO terms are detailed in Tables S15-S16. FDR False discovery rate