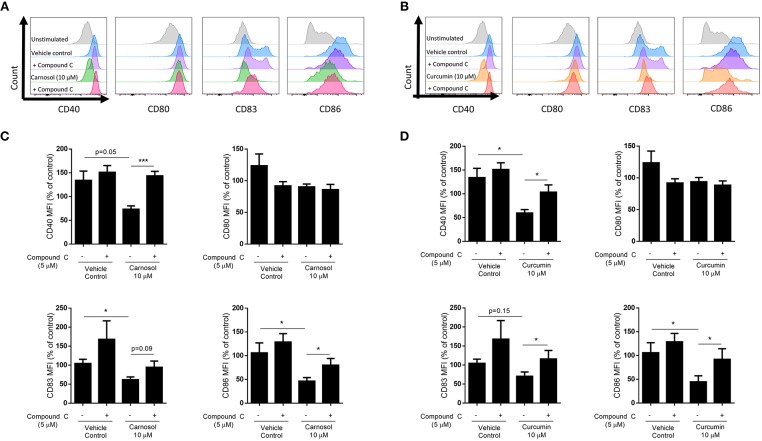
Figure 4.
Inhibition of AMPK attenuates reduction of DC maturation markers by carnosol and curcumin. Primary human DC (n = 7) were incubated with or without compound C (5 μM) for 1 h prior to treatment with carnosol (10 μM), curcumin (10 μM), or a vehicle control for 6 h. DC were then stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) and expression of maturation markers CD40, CD80, CD83, and CD86 was determined after 24 h by flow cytometry. Histograms depict expression of maturation markers in DC treated with (A) carnosol or (B) curcumin, with or without compound C, compared to controls from one representative experiment. Pooled data (n = 7) depicts expression of CD40, CD80, CD83, and CD86 in DC treated with (C) carnosol or (D) curcumin, with or without compound C. Results shown are mean (± SEM) of the measured Mean Fluorescence Intensities (MFI), expressed as percentages of the vehicle control. Statistical significance was determined by repeated measures one-way ANOVA, with Sidak's multiple comparisons post hoc test to compare pre-selected group pairs (***p < 0.001, *p < 0.05).