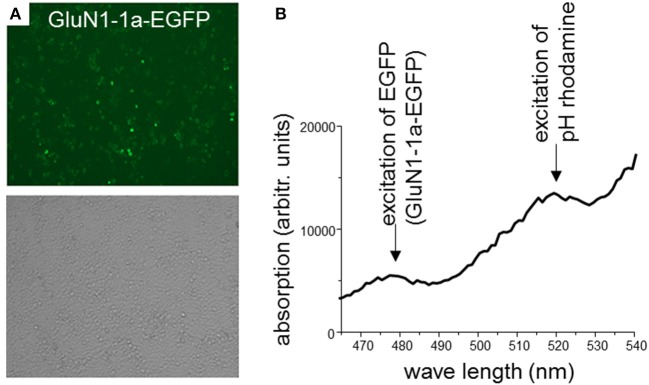
Figure 2.
(A) HEK 293T cells co-expressing rat GluN1-1a-EGFP and GluN2B-ECFP. 2 days after transfection, expression of fluorescently labeled NMDARs was verified using confocal laser-scanning microscopy. About 70–80% of the cells expressed GluN1-1a-EGFP as subunit putatively targeted by the GluN1-aAbpH−rhod (upper panel) and GluN2B-ECFP (data not shown). Light microscopy demonstrates typical cell densities (lower panel). (B) Binding of GluN1-aAbpH−rhod to the NMDAR subunits as determined by the plate reader experiment. HEK 293T cells expressing GluN1-1a-EGFP/GluN2B-ECFP were incubated with GluN1-aAbpH−rhod on ice in 96-well-plates. GluN1-1a-EGFP and GluN1-aAbpH−rhod fluorescence was excited at wavelengths of 480 nm and 520 nm and emission measured at wavelengths of 510 and 580 nm, respectively, verifying the GluN1-1a-EGFP expression and the binding of GluN1-aAbpH−rhod.