Figure 5.
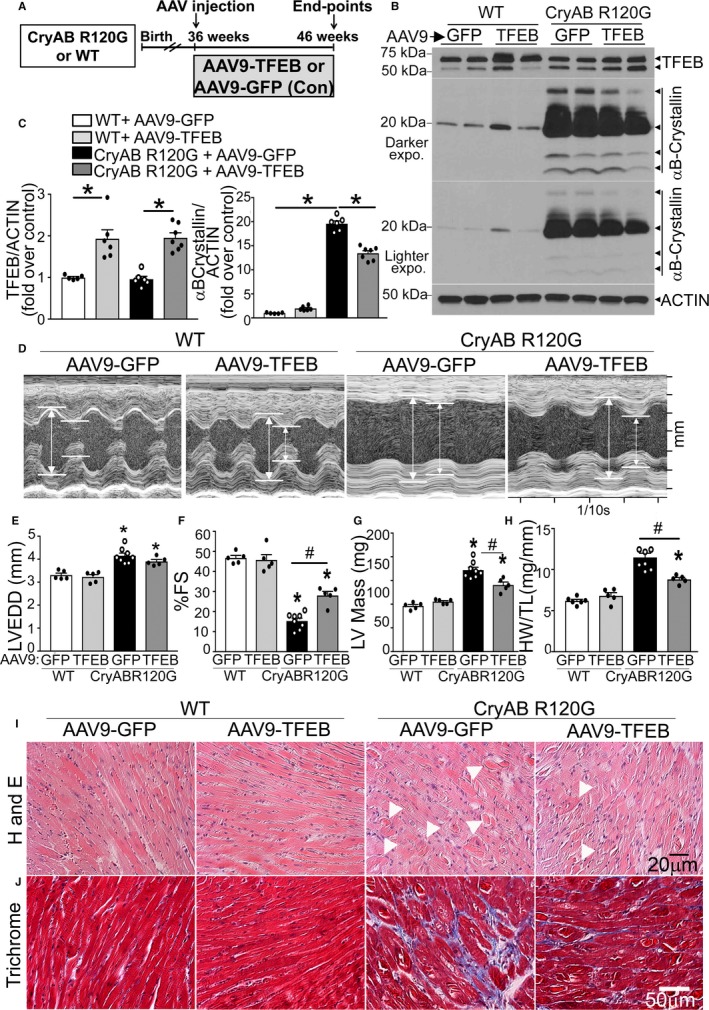
Adeno‐associated virus (AAV9)–mediated transcription factor EB (TFEB) transduction rescues cardiomyopathy in αB‐crystallin R120G mutant transgenic mice and promotes removal of protein aggregates. A, Schematic depicting experimental intervention with AAV9‐mediated TFEB transduction (or AAV9–green fluorescent protein [GFP] as control) in Myh6‐CryABR120G transgenic mice or littermate controls. B and C, Representative immunoblots demonstrating expression of TFEB in total protein extracts with quantitation (C, left) and αB‐crystallin (C, right) in hearts from Myh6‐CryABR120G transgenic mice or littermate wild‐type (WT) mice transduced with AAV9‐TFEB or AAV9‐GFP as in A, at 46 weeks of age. N=5 to 7/group. D through H, Representative 2‐dimensional–directed M‐mode echocardiograms (D) in Myh6‐CryABR120G transgenic mice or littermate WT mice transduced with AAV9‐TFEB or AAV9‐GFP as in A, at 46 weeks of age, with quantitation of left ventricular end‐diastolic diameter (LVEDD; E), left ventricular percentage endocardial fractional shortening (LV %FS; F), LV mass (G), and heart weight normalized to tibial length (HW/TL; H) in mice treated as in A. N=5 to 8/group. A total of 1 of 9 AAV9‐GFP–injected and 1 of 6 AAV9‐TFEB–injected Myh6‐CryABR120G transgenic mice died during the study. See Table S3 for additional echocardiographic data on these mice. I and J, Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H and E; I) and trichrome (J) stained myocardial sections from mice treated as in A. Arrowheads point to eosinophilic aggregates in I. *P<0.05 by post hoc test after 1‐way ANOVA.
