Figure 3.
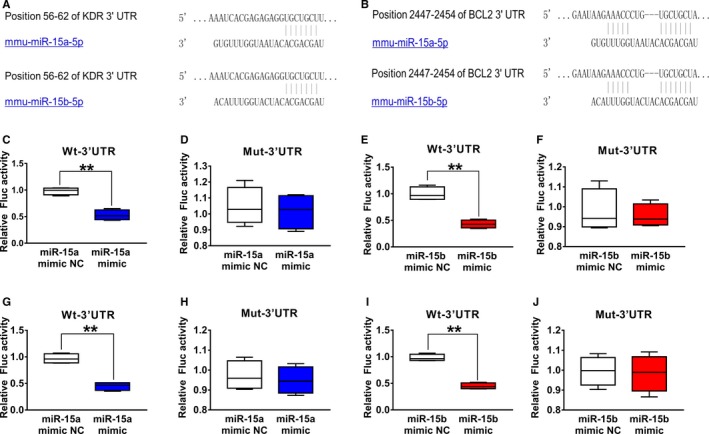
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR‐2) and Bcl‐2 were validated as a target of miR‐15a/15b. A, The 3′‐untranslated region (UTR) of VEGFR‐2 harbored a potential targeting site of miR‐15a/15b, which was conserved among mouse by bioinformatics analysis. C and E, Luciferase assay was performed to show that overexpression of miR‐15a/15b in HEK 293T cells could significantly suppress the luciferase activity of a reporter fused with 3′‐UTR of VEGFR2 mRNA. HEK 293T cells were transfected with a pMIR‐VEGFR2‐3′‐UTR or pMIR‐VEGFR2‐m3′‐UTR. Meanwhile, the cells were cotransfected with an miR‐15a/15b mimics or mimics negative control (NC). Compared with the mimics NC, the miR‐15a/15b mimics could reduce luciferase activity containing a wild‐type miR‐15a/15b binding site (C and E) but not a mutant binding site (D and F). B, 3′‐UTR of Bcl‐2 harbored a potential targeting site of miR‐15a/15b, which was conserved among mouse by bioinformatics analysis. G and I, Luciferase assay was performed to show that overexpression of miR‐15a/15b in HEK 293T cells could significantly suppress the luciferase activity of a reporter fused with 3′‐UTR of Bcl‐2 mRNA. HEK 293T cells were transfected with a pMIR‐Bcl‐2‐3′‐UTR or pMIR‐Bcl‐2‐m3′‐UTR. Meanwhile, the cells were cotransfected with an miR‐15a/15b mimics or mimics NC. Compared with the mimics control, the 15a/15b mimics could reduce luciferase activity containing a wild‐type miR‐15a/15b binding site (G and I) but not a mutant binding site (H and J). **P<0.01 vs mimics NC.
