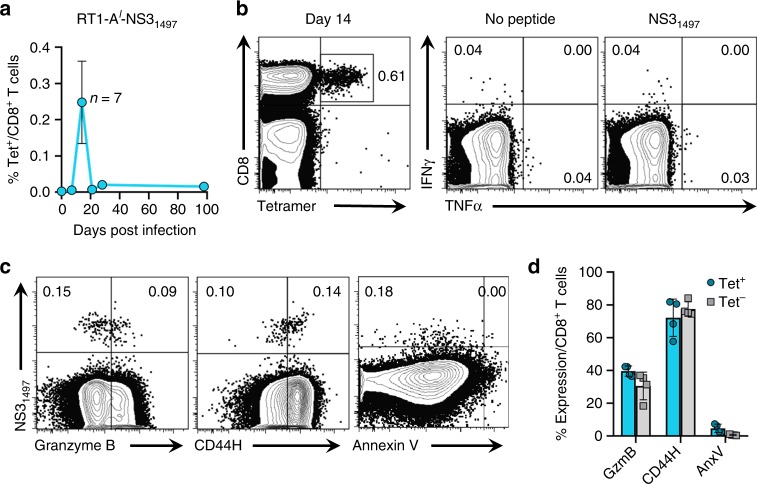
Fig. 2.
Expansion of non-functional RHV-specific CD8+ T cells during infection. Lewis rats were challenged intravenously with 106 genomes of RHV and intrahepatic CD8+ T cell responses to the RT1-Al-restricted NS31497 epitope were assessed by class I tetramer and cytokine production assays. a Frequency of intrahepatic CD8+ T cells specific to NS31497 epitope at the indicated time post infection. Data from n = 3–7 rats per timepoint are shown (mean±SEM). b Sample flow plots showing frequency of intrahepatic NS31497-specific CD8+ T cells at day 14 when analyzed by tetramer staining (left) versus production of intracellular cytokines (right). For stimulation, cells were pulsed for 5-h with minimal peptide (10 µg/mL). c Representative flow plots of intrahepatic CD8+ T cells stained with NS31497 tetramer and antibodies against granzyme B, CD44H, and annexin V at day 14. d Calculated frequencies of granzyme B (GzmB), CD44H, and Annexin V (AnxV) expressing cells within the tetramer (Tet) positive (blue circles) and negative (gray squares) CD8+ T cell populations 14 days post infection. Data from n = 4 rats are shown (mean ± SEM). Numbers within all FACS plots indicate the frequency of positive cells within the CD8+ T cell gate